Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Interleukin-17 in inflammatory skin disorders — extra information
Interleukin-17 in inflammatory skin disorders
Author: Anoma Ranaweera, Medical Writer, New Zealand. Editor in Chief: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. October 2019.
Introduction - interleukin-17 Introduction - interleukin-17 pathway Protective role of interleukin-17 Skin disease involvement Future indications
What is interleukin-17?
Interleukin (IL)-17 refers to a family of proteins that play critical roles against bacterial infections and fungal infections and in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases.
The IL-17 cytokine family consists of six cytokines (interleukins 17A to 17F) and five receptors (interleukins 17RA to 17RE). The interleukins 17A, 17F, and 17A/F heterodimer ligands share a common receptor subunit (interleukin-17RA) for signalling.
IL-17 is mainly produced by a subset of CD4 cells named Th-17 (T–helper 17) cells. It is mainly secreted by activated CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes, while its receptor is found on many cell types.
What is the interleukin-17 pathway?
IL-17 has been classified as a pro-inflammatory cytokine because it induces the expression of mediators of inflammation involved in the proliferation, maturation, and chemotaxis of neutrophils.
- IL-17A and IL-17F are protective against infections on the epithelial surfaces of the skin, lung, and oral cavity [1,2]
- Signalling downstream of IL-17RA/RC elicits the expression of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs), including beta-defensins
- IL-17 acts with IL-22 (produced mainly by T-helper 22 cells in humans) to induce expression of AMPs by keratinocytes [3]
- IL-17A and IL-17F induce cytokines such as:
- Interleukin (IL)-6
- G-CSF (granulocyte colony-stimulating factor)
- GM-CSF (granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor)
- IL-1β (interleukin 1 beta)
- TGF-β (transforming growth factor-beta)
- TNF-α (tumour necrosis factor-alpha)
- Chemokines, such as IL-8
- Prostaglandins, such as PGE2
- Matrix metalloproteinases (MMP) [3].
Overproduction of interleukins 17A, 17F, and 17A/F is associated with tissue damage and autoimmune diseases such as:
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Multiple sclerosis (MS)
- Crohn disease
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Inflammatory skin diseases such as:
Skin diseases associated with interleukin-17
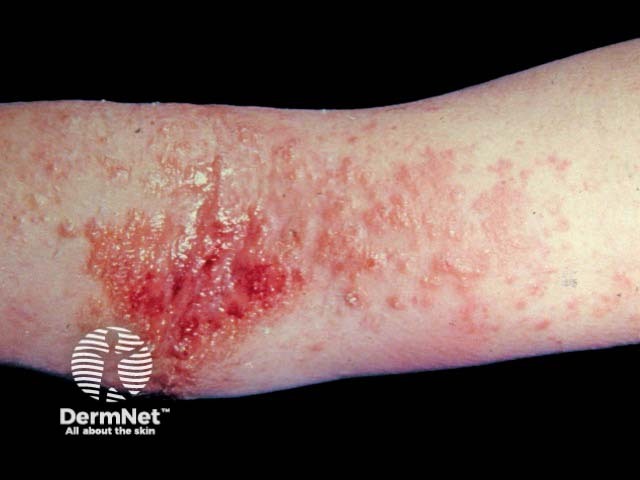
Atopic eczema
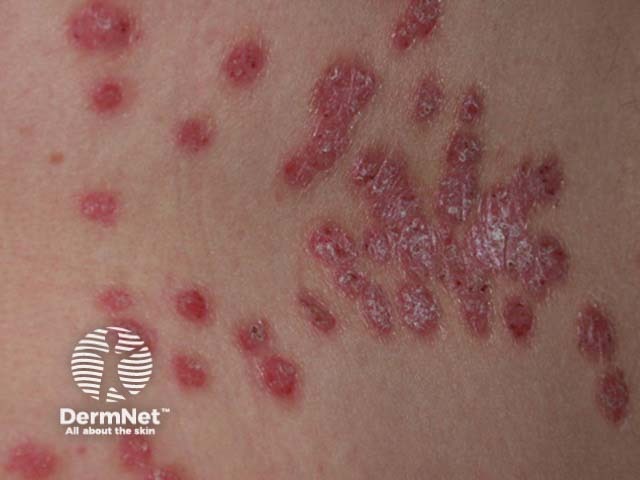
Chronic plaque psoriasis
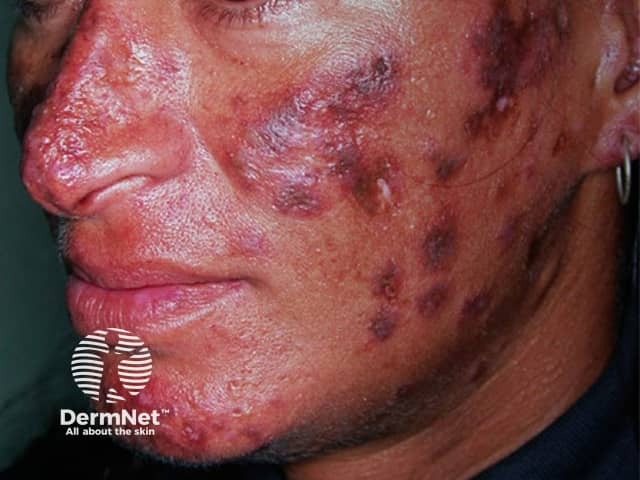
Cutaneous lupus erythematosus
What is the protective role of interleukin-17 against infections?
The IL-17 family of cytokines play a role in the management of pathogens.
- IL-17F, IL-17A, and IL-17C are important for protection against Staphylococcus aureus (a cause of impetigo) and Candida albicans at epithelial surfaces [5].
- Therapies that block IL-17A and IL-17RA signals have the potential to exacerbate bacterial and fungal infections [6].
The same cytokines have also been reported to have functions outside the skin, at least trials involving mice. IL-17E has a protective role in CNS inflammation and participates in protective responses against parasites in the intestine [7–9].
Infections protected by IL-17
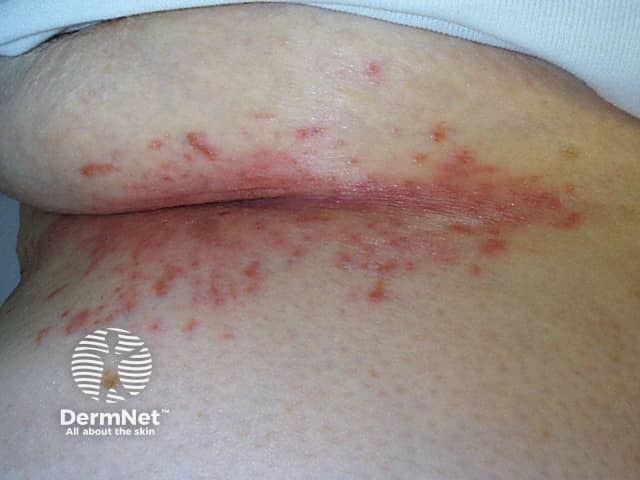
Candida intertrigo
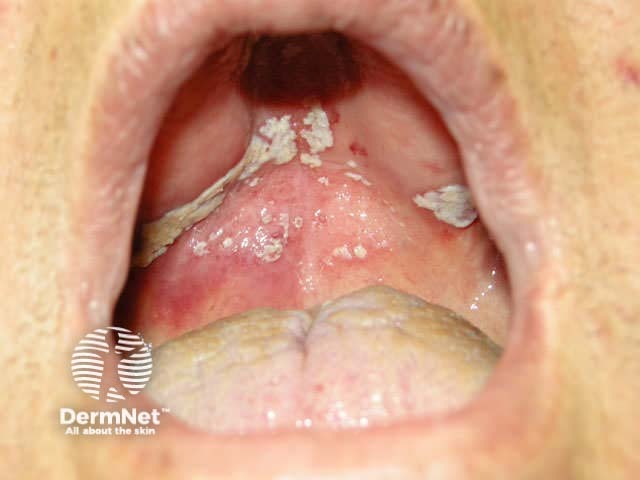
Oral candidiasis
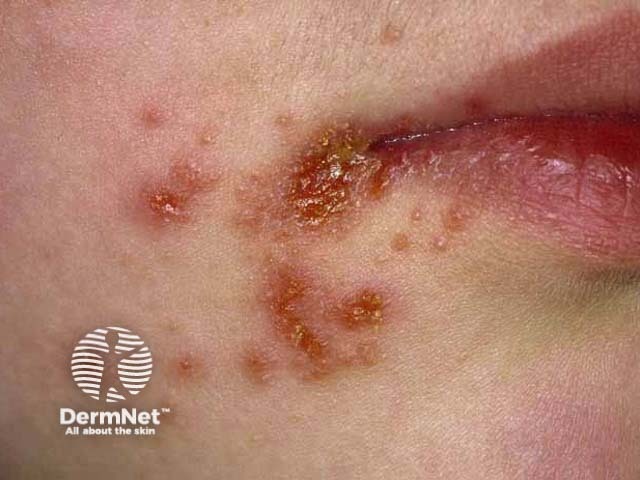
Impetigo
What skin diseases involve interleukin-17?
Skin diseases in which interleukin-17 is involved or is thought to be involved are as follows.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterised by epidermal hyperplasia.
- Elevated IL-17A and Th17-related cytokines, such as IL-22 and IL-23, are found in psoriatic plaques.
- The IL-17A-blocking monoclonal antibodies secukinumab and ixekizumab and the IL-17RA-targeting antibody brodalumab result in marked improvement and sometimes complete clearance of psoriasis [10–12].
- Bimekizumab has a high affinity for IL-17A and IL-17F, selectively binding and inhibiting the activity of both isoforms.
- Several other molecules targeting the IL-17 family are in clinical development, as are drugs targeting IL-23, which is upstream of IL-17, and signalling molecules, which are downstream [13,14].
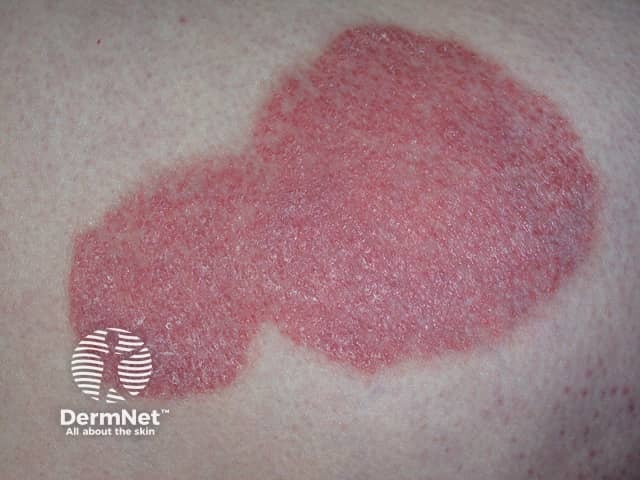
Chronic plaque psoriasis
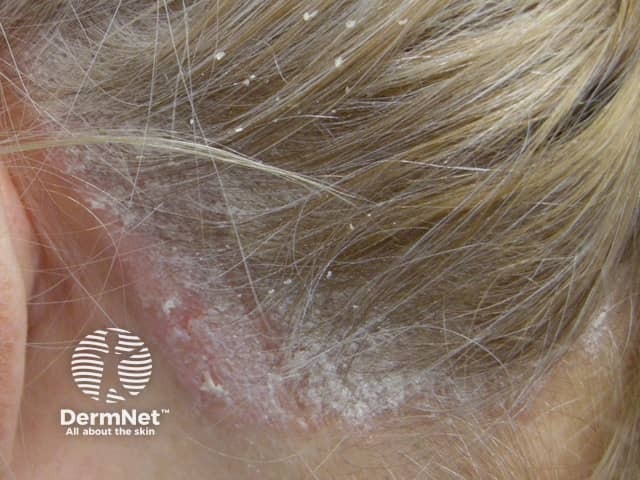
Scalp psoriasis
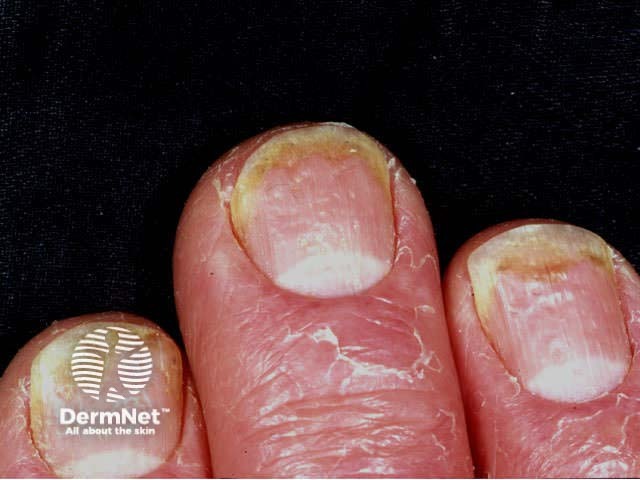
Nail psoriasis
Dermatitis
The role of IL-17 is under investigation in various forms of dermatitis.
- Serum levels of IL-17A and F are increased in children with atopic dermatitis and are correlated with disease severity.
- Expression of IL-17A at the mRNA level is increased in the skin of patients with allergic contact dermatitis due to nickel allergy [15].
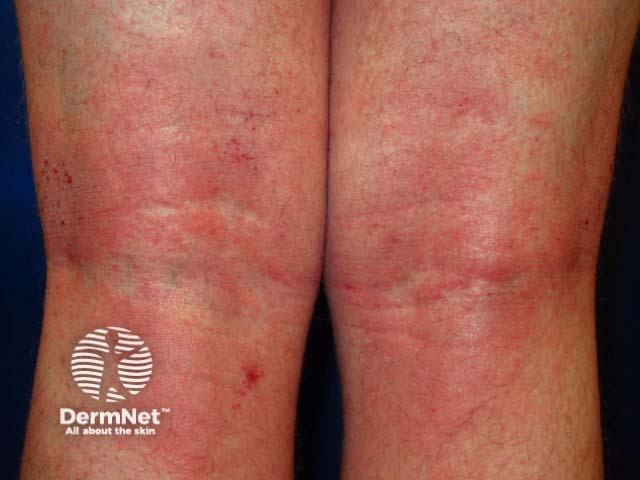
Atopic dermatitis
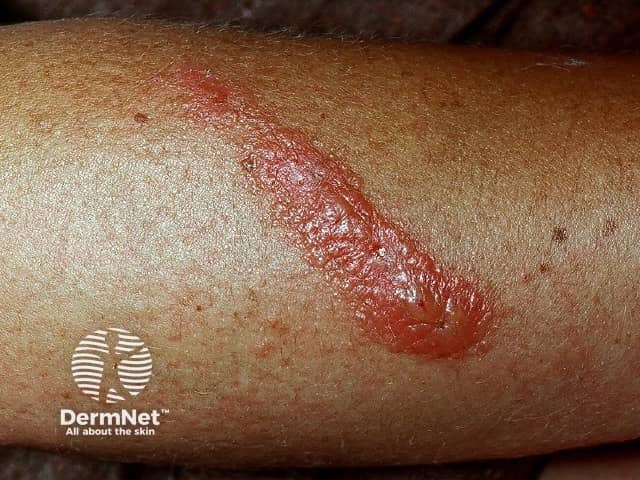
Plant contact dermatitis
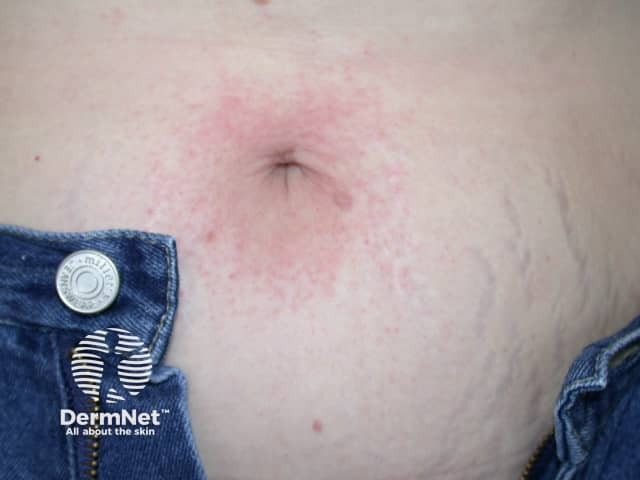
Nickel dermatitis
Skin cancer
IL-17 signalling has been associated with the development of skin cancer during chemical carcinogenesis in mouse models.
- This pro-tumourigenic effect of IL-17 is thought to occur via the promotion of epithelial proliferation and the anti-apoptotic effect of the transcription factor STAT-3 (Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3), which may be downstream of IL-17-induced genes such as IL-6.
- IL-17A blockade may prove useful for controlling at least some cancers [16]. This is unproven in humans
Epithelial skin cancers
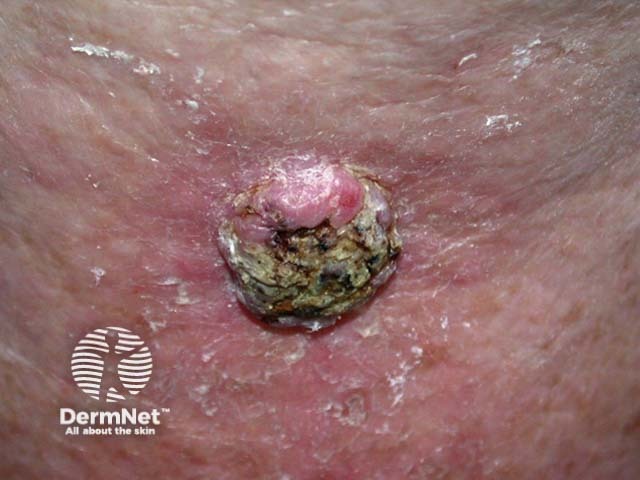
Squamous cell carcinoma of limbs
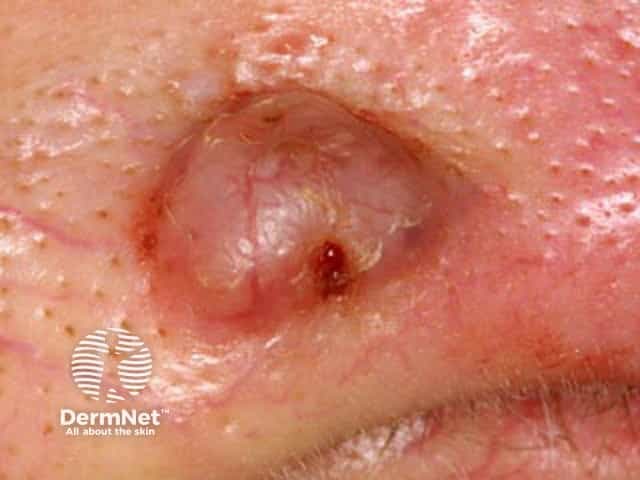
Basal cell carcinoma affecting the nose
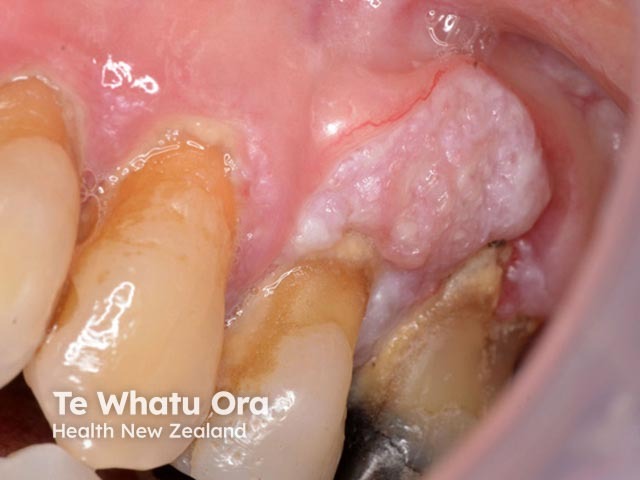
Oral cancer
What are the future indications of the study of interleukin-17?
The proinflammatory properties of IL-17 are protective against infection. A good understanding of the different roles played by the IL-17 cytokines is necessary to design effective drugs relating to pathogenesis and mechanisms of inflammation.
- Unrestrained IL-17 signalling is associated with immunopathology, autoimmune disease, and cancer progression.
- IL-17 inhibitors are proving valuable in the control of inflammatory skin disease.
- Analysis of the roles of individual components of the IL-17 pathway in infection and inflammation is ongoing.
References
- Ye P, Garvey PB, Zhang P, et al. Interleukin-17 and lung host defense against Klebsiella pneumoniae infection. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001;25(3):335–40. doi:10.1165/ajrcmb.25.3.4424. PubMed
- Dubin PJ, Martz A, Eisenstatt JR, Fox MD, Logar A, Kolls JK. Interleukin-23-mediated inflammation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pulmonary infection. Infect Immun. 2012;80(1):398–409. doi:10.1128/IAI.05821-11. PubMed
- Shen F, Gaffen SL. Structure-function relationships in the IL-17 receptor: implications for signal transduction and therapy. Cytokine. 2008;41(2):92–104. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2007.11.013. PubMed Central
- Monin L, Gaffen SL. Interleukin 17 family cytokines: signaling mechanisms, biological activities, and therapeutic implications. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2018;10(4):a028522. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a028522. PubMed
- Reynolds JM, Martinez GJ, Nallaparaju KC, Chang SH, Wang YH, Dong C. Cutting edge: regulation of intestinal inflammation and barrier function by IL-17C. J Immunol. 2012;189(9):4226–30. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1103014. PubMed
- Ishigame H, Kakuta S, Nagai T, et al. Differential roles of interleukin-17A and -17F in host defense against mucoepithelial bacterial infection and allergic responses. Immunity. 2009;30(1):108–19. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2008.11.009. PubMed
- Kleinschek MA, Owyang AM, Joyce-Shaikh B, et al. IL-25 regulates Th17 function in autoimmune inflammation. J Exp Med. 2007;204(1):161–70. doi:10.1084/jem.20061738. PubMed
- Angkasekwinai P, Srimanote P, Wang YH, et al. Interleukin-25 (IL-25) promotes efficient protective immunity against Trichinella spiralis infection by enhancing the antigen-specific IL-9 response. Infect Immun. 2013;81(10):3731–41. doi:10.1128/IAI.00646-13. PubMed
- Owyang AM, Zaph C, Wilson EH, et al. Interleukin 25 regulates type 2 cytokine-dependent immunity and limits chronic inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract. J Exp Med. 2006;203(4):843–9. doi:10.1084/jem.20051496. PubMed
- Kikly K, Liu L, Na S, Sedgwick JD. The IL-23/Th(17) axis: therapeutic targets for autoimmune inflammation [published correction appears in Curr Opin Immunol. 2007 Feb;19(1):111]. Curr Opin Immunol. 2006;18(6):670–5. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2006.09.008. PubMed
- Griffiths CE, Reich K, Lebwohl M, et al. Comparison of ixekizumab with etanercept or placebo in moderate-to-severe psoriasis (UNCOVER-2 and UNCOVER-3): results from two phase 3 randomised trials. Lancet. 2015;386(9993):541–51. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60125-8. PubMed
- Papp KA, Langley RG, Sigurgeirsson B, et al. Efficacy and safety of secukinumab in the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II dose-ranging study. Br J Dermatol. 2013;168(2):412-21. doi:10.1111/bjd.12110. PubMed
- Conrad C, Gilliet M. Psoriasis: from pathogenesis to targeted therapies. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018;54(1):102–13. doi:10.1007/s12016-018-8668-1. PubMed
- Glatt S, Baeten D, Baker T, et al. Dual IL-17A and IL-17F neutralisation by bimekizumab in psoriatic arthritis: evidence from preclinical experiments and a randomised placebo-controlled clinical trial that IL-17F contributes to human chronic tissue inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(4):523–32. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212127. PubMed
- He D, Wu L, Kim HK, Li H, Elmets CA, Xu H. CD8+ IL-17-producing T cells are important in effector functions for the elicitation of contact hypersensitivity responses. J Immunol. 2006;177(10):6852–8. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.177.10.6852. PubMed
- Wang L, Yi T, Zhang W, Pardoll DM, Yu H. IL-17 enhances tumor development in carcinogen-induced skin cancer. Cancer Res. 2010;70(24):10112-10120. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-0775. PubMed
On DermNet
