Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Hair replacement surgery — extra information
Introduction Patient selection Techniques Transplantation process Complications Other types A cosmetic alternative
What is hair replacement surgery?
Hair replacement surgery is the surgical movement of 'permanent' hair along with its roots to an area of bald or balding skin. There are several surgical techniques available but the method most often used today is hair transplantation.
Patient selection for hair transplantation
Hair transplantation is used predominantly to treat the hereditary balding condition known as androgenetic alopecia (male pattern hair loss or less often, female pattern hair loss). Patients with male pattern hair loss tend to have 'lifetime' hair on the sides and back of the head, which are used as donor sites in transplantation.
Hair transplantation does not work on alopecia areata as the transplanted hair will not grow in the area.
Hair transplantation techniques
Hair transplantation involves removing small pieces of hair and follicles from the donor area (usually hair on the back and sides of the head) and relocating them to the bald or thinning area. The transplantation is a long and complex procedure that involves two distinct processes: donor harvesting and the preparation of recipient sites.
Donor harvesting
It is important to only harvest protected hair follicles to ensure their survival when transplanted. The hair on the back and sides of the head is known as donor dominant or lifetime hair and when moved will continue to grow as it would have in its original site.
There are several different techniques used to harvest hair follicles.
Technique |
Procedure |
|
|---|---|---|
Punch harvesting |
|
|
Excision |
|
|
Strip harvesting |
|
|
Once the donor tissue is harvested, they may be transplanted directly (grafts obtained by punch harvesting) or cut into smaller grafts. The shape and size of the grafts is one of the key factors in the final outcome of hair transplantation. Grafts containing fewer hairs usually provide better results as there is less clumping of hair as it starts to regrow. Graft shapes and sizes include:
- Punch grafts – round grafts containing about 10–15 hairs. These may be further cut in half or quarters to get smaller grafts.
- Mini-grafts – smaller grafts containing 2–4 hairs dissected from excised or strip harvested grafts.
- Micro-grafts – tiny grafts containing 1–2 hairs. Also referred to as follicular unit grafting or follicular transfer.
- Slit grafts – thin grafts containing 4–10 hairs.
Preparation of recipient sites
Several techniques are used to prepare the recipient sites for where grafts are to be placed. Once the sites are prepared small forceps or needles are used to grasp the graft and gently insert it into place.
Technique |
Procedure |
|
|---|---|---|
Single hair and slit grafting |
|
|
Dilation (modified slit grafting) |
|
|
Punch grafting |
|
|
Laser-assisted grafting |
|
|
Hair transplantation process
Hair transplantation is done in a doctor's office and can take between 4 to 8 hours depending on the extent of the transplantation.
Traditionally, hair transplantation has been performed in multiple planned sessions that are spaced 3-6 months apart. A typical session might average between 150 and 300 grafts. However, more recently the trend is to place more grafts per session. It is not uncommon for sessions to involve 750 to 2000 grafts. The purported benefit of these 'mega sessions' is a reduced number of hair transplantation visits to achieve hair restoration in a shorter period of time. The possible downfall is reduced overall graft survival where grafts are packed very close together.
The procedure is usually done under local anaesthetic and does not cause too much discomfort. In most cases, immediately after the hair transplant the hairs fall out of the grafts and do not regrow for 1–3 months. The donor sites gradually heal to leave slight scarring but this is concealed by “lifetime” hair growing around the site. Patients need to be aware that hair transplantation does not produce an instantaneous head of hair but the results are seen over time.
Complications of hair transplantation
Hair transplantation is a surgical procedure so complications can and do occur as with any other surgical procedure. Possible complications include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Numbness
- Pain
- Swelling of the forehead and/or face (expected but can be severe)
- Scarring at donor site or recipient site
- Poor or no growth of grafts
- An unnatural appearance of transplanted hair.
The areas affected by balding are likely to progress.
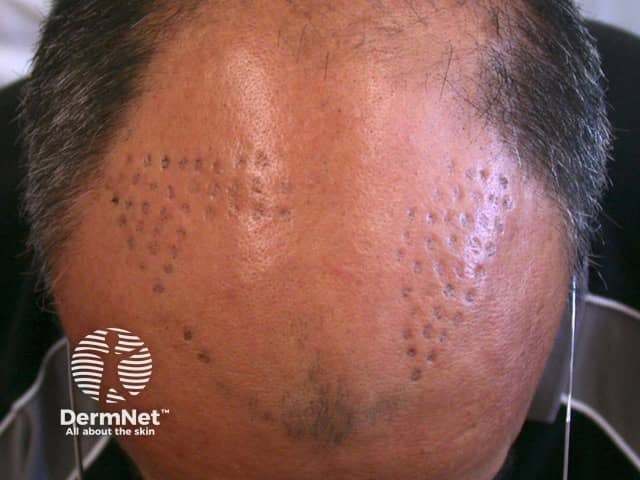
Hair transplants
Other types of hair replacement surgery
The following techniques are still performed although they have largely been replaced by hair transplantation.
- Flaps
- Scalp reduction
- Scalp expansion and scalp extension
- Tissue expansion
These techniques produce a more dramatic and instantaneous result but are becoming less popular because of the following reasons:
- More extensive surgical procedures that usually require general anaesthesia
- Procedure is more painful and post-operative care is much greater
- Severe and visible scarring is common with scalp surgery
- Unnatural looking growing hair, particularly years after the actual surgery
A cosmetic alternative to hair replacement
Hair loss can be hidden without surgery. Techniques include:
- Scalp micropigmentation to mimic shaven hair or disguise scars (scalp tattoo)
- Wigs and hair pieces
- Electrostatic microfibres used to bulk up natural hair
- Hairstyling to cover balding areas
References
- Hair Transplantation – Medscape Reference
On DermNet
- Hair loss
- Male pattern hair loss
- Female pattern hair loss
- Alopecia areata
- Psychological effects of hair loss
Other websites
- Medscape Reference:
- Androgenetic alopecia US National Library of Medicine Genetics Home Reference
- Howstuffworks: How Hair Replacement Works
