Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Fragrances and perfumes — extra information
Fragrances and perfumes
Author: Dr Daniel Mazzoni, Junior Medical Officer, Royal Brisbane and Women’s Hospital, Brisbane, QLD, Australia. DermNet Editor in Chief: Adjunct A/Prof. Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. January 2020.
Introduction
Types of perfume
Manufacture
Ingredients and chemical structures
Uses
Adverse effects
Differences in marketing
What do the terms 'fragrance-free' and 'unscented' mean?
What are fragrances and perfumes?
A fragrance is defined as a combination of organic compounds that produces a distinct smell or odour.
A perfume is a liquid mixture used to emit a pleasant odour. It is formed from fragrant essential oils derived from plants and spices or synthetic aromatic compounds.
Cosmetic fragrances applied to a person’s body to emit a pleasant smell include perfume, cologne, and aftershave [1].

Perfume store

Perfume shelf

Glass perfume bottle
What are the different types of perfume?
Perfumes are classified into 5 main groups loosely based on their concentration of aromatic compounds.
Parfum or extrait has a 20–30% concentration of fragrance.
- As parfum contains a high concentration of fragrance, it is typically the most expensive.
- It is usually a heavier, oilier product than the other types of perfume, and tends to be used more sparingly.
- The smell is long-lasting — an average of 8 hours and up to 24 hours.
Eau de parfum or parfum de toilet has a 15–20% concentration of fragrance.
- Eau de parfum contains a greater concentration of alcohol and water and is generally cheaper than parfum.
- It is a lighter product and has a shorter duration of around 4 to 5 hours.
- Eau de parfum is the most common fragrance type and is the base for other fragrance types.
Eau de toilette has a 5–15% concentration of fragrance.
- Eau de toilette has a low concentration of essential oils and a high concentration of alcohol.
- It dissipates quickly and lasts 2 to 3 hours.
- It is a cheaper option and often used for daywear.
Eau de cologne has a 2–4% concentration of fragrance.
- Eau de cologne has a much lower fragrance concentration to create a very light formulation.
- It is primarily used in fragrances designed for males as an aftershave or splash-on fragrance.
- It dissipates quickly and lasts about 2 hours.
- Cologne, by definition, refers to ‘eau de cologne’. However, the term ‘cologne’ is in common use in the English language to denote any fragrance worn by a male [2].
Eau fraiche has a 1–3% concentration of fragrance.
- Eau fraiche has the lowest fragrance concentration of all types of parfum, and is diluted with water rather than alcohol or oil.
- Common uses for eau fraiche include mists, splashes, and veils that are very light and dissipate within an hour [2].
Fragrances are also added to many cosmetics and household goods.
Cosmetics listing fragrance ingredients
How is perfume manufactured?
The perfume manufacturing process for natural essences involves collection, extraction, blending and ageing of the product [3].
Collection
- In the collection stage, initial ingredients are obtained from various plant substances and the fatty extracts of animal products [4].
Extraction
- Distillation is the most commonly used method to extract perfume. In steam or dry distillation, the material is heated to high temperatures and condensed into gas to release the desired essential oils, which are then cooled and liquefied. Water distillation is more effective for some more delicate materials, in which plant material is placed into boiling water.
- In solvent extraction, the material is added to a solvent, which forms a waxy aromatic compound that is then mixed with alcohol to release the essential oils. This method is becoming less commonly used as it is costly and time-consuming.
- Expression means the material is compressed and the oils are mechanically squeezed out. This method is primarily used for fresh fruit rinds and thermally labile components.
- In maceration, the material is soaked in carrier oils serving as solvents, which capture heavier, larger plant molecules. This method is useful for materials which require a higher yield of essential oils.
- In enfleurage, the material is drawn out into a fat or oil base and then extracted with alcohol. Enfleurage is no longer used commercially [3,4].
Blending
- Oils are blended according to a particular formula using multiple different ingredients.
- The scent is mixed with alcohol; the volume of alcohol used depends on the intended type of perfume [4].
Ageing
- It takes months to years after the scent has been blended to achieve the desired scent. This ageing period allows the ongoing blending of the selected chemicals to modify the scent [4].
Other perfumes are synthetically manufactured in laboratories. While the need to obtain natural ingredients is avoided, achieving the desired scent can be more challenging [3].
What are the ingredients and chemical structures of perfume?
Perfumes are composed of three structural parts — the head, middle, and base notes — to provide the first impression, body, and lasting impression of the fragrance respectively after the application of a perfume. The presence of one note may alter the perception of another.
The head note, or top note, provides the initial scent that forms the first impression of the perfume. It has the following features:
- It is comprised of small light molecules that have a strong fresh scent but evaporate quickly, usually 5–30 minutes after application.
- Common top notes include citrus (lemon, orange), light fruits (berries), and herbs (sage, lavender) [3,5].
The middle note, or heart note, masks any unpleasant initial impression of the base note and provides the main body of the scent.
- It is comprised of more complex molecules than top notes and has a more mellow, rounded, and balancing scent.
- It first appears 20–60 minutes after application, and usually lasts 2–4 hours.
- Tones are made from more potent florals and spices. Common middle notes include lemongrass, rose, geranium, jasmine, nutmeg, lavender, cinnamon, and coriander [3,5].
The base note adds to the middle note to boost and deepen the existing body of the scent and provide its lasting impression.
- It is comprised of large heavy molecules to provide a rich and smooth nature to the scent.
- It is typically not perceived until 30 minutes after application or during the dry-down period. Some can last over 24 hours after application.
- Common base notes include cedarwood, sandalwood, vanilla, amber, patchouli, oakmoss, and musk [3,5].
Why is perfume used?
Perfume is used to give a pleasant and desirable scent to a person’s body, typically with the aim of increasing self-appeal and self-confidence.
Scents are reported to enhance health and well-being by improving mood, reducing anxiety and stress, increasing cognitive function, and improving sleep [6].
A link has also been identified between pleasant scents and improved pain tolerance through the activation of opioid pathways.
What are the adverse effects of perfume?
Adverse effects of perfume primarily involve irritant and allergic reactions.
The use of perfume directly exposes skin to various chemicals, which are then absorbed. The chemical substances in some fragrances can cause contact allergic dermatitis in sensitised individuals. Studies have reported that one-third of the general population experience at least one adverse health effect from fragranced products [7].
Common adverse effects may include:
- Headaches
- Eye, nose, and throat irritation
- Nausea
- Irritant and allergic contact dermatitis (see fragrance mix allergy)
- Asthma flares.
Irritant contact dermatitis is due to repeated or excessive exposure to irritating chemicals in the fragrance, usually over a significant period of time. It presents as localised erythema at the site of exposure, dry cracked skin, and blisters and erosions in severe cases.
Allergic contact dermatitis is a delayed hypersensitivity reaction and may occur after just one, or more frequently, many exposures. Symptoms are similar to irritant contact dermatitis, but tiny quantities may be sufficient to cause allergy. It may also result in dermatitis in sites that were not directly exposed to the fragrance.
Allergic contact dermatitis is confirmed by patch testing.
Cosmetic products do not legally require allergen labelling, unlike foods [1].
Contact allergic dermatitis to fragrance
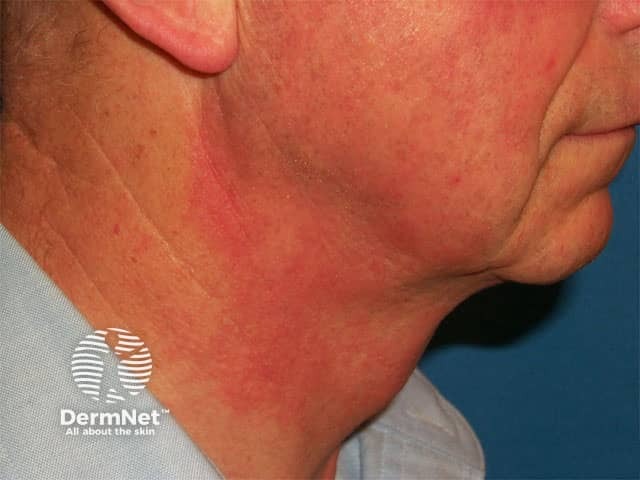
Contact allergy to fragrance in aftershave
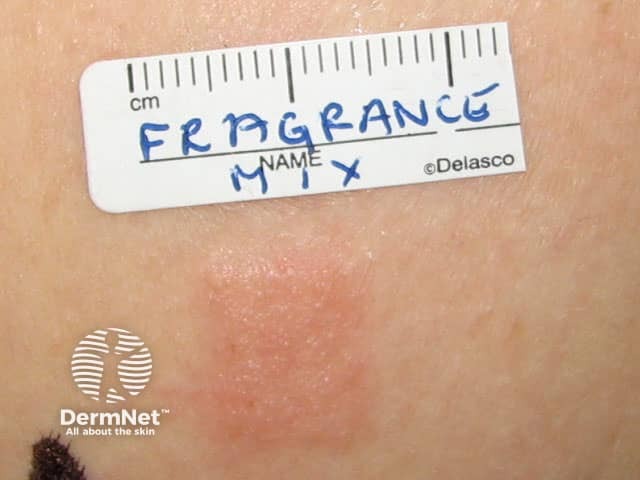
Positive patch test to fragrance
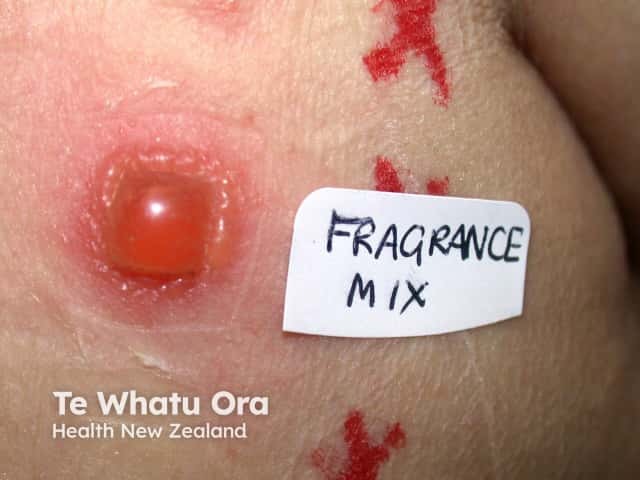
What is the difference between perfumes marketed to males and females?
‘Pour homme’ and ‘pour femme’ are French terms used to denote perfumes intended for males and females respectively.
The difference is based on contemporary cultural and marketing trends. Perfumes that emit oriental, woody, and musky scents are typically marketed as masculine perfumes, whereas fruity and floral scents are typically more feminine.
What do the terms ‘fragrance-free’ and ‘unscented' mean?
Fragrance-free products do not use fragrance materials for the specific purpose of imparting scent; however, they may contain fragrance ingredients intended for therapeutic uses such as to relieve muscle aches or help with sleep.
Unscented products contain chemicals that neutralise or mask the odours of other ingredients.
Fragrance-free claims

References
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Cosmetics. Available at: www.fda.gov/cosmetics/productsingredients/ingredients/ucm388821.htm (accessed March 2019)
- Perfume.com. A Guide to Perfume Types. Available at: www.perfume.com/article-a-guide-to-perfume-types (accessed March 2019).
- Surburg H, Panten J. Common Fragrance and Flavor Materials: Preparation, Properties and Uses (6th edn). Wiley, 2016.
- How products are made. Perfume. Available at: www.madehow.com/Volume-2/Perfume.html (accessed March 2019).
- Poucher, WA. Poucher’s Perfumes, Cosmetics and Soaps (9th edn). Springer, 1993.
- Sowndhararajan K, Kim S. Influence of fragrances on human psychophysiological activity: with special reference to human electroencephalographic response. Sci Pharm. 2016 Nov 29;84(4):724-51. doi: 10.3390/scipharm84040724. PMID: 27916830; PMCID: PMC5198031. PubMed
- Steinemann A. Health and societal effects from exposure to fragranced consumer products. Prev Med Rep. 2016 Nov 14;5:45-7. doi: 10.1016/j.pmedr.2016.11.011. PMID: 27896043; PMCID: PMC5122698. Journal
On DermNet
- Fragrance mix allergy
- Fragrance allergy
- Allergic contact dermatitis to essential oils
- Contact dermatitis
- Cosmetics allergy
