Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Contact allergy to lauryl glucoside — extra information
Contact allergy to lauryl glucoside
Last reviewed: March 2023
Author: Dr Moushumi Das, Medical Registrar, Waikato Hospital, New Zealand (2023)
Reviewing dermatologist: Dr Ian Coulson
Edited by the DermNet content department
Introduction
Locations
Demographics
Features
Diagnosis
Testing
Treatment
What is lauryl glucoside?
Lauryl glucoside is an alkyl glucoside primarily used as a surfactant in common cosmetic, skincare, and household products. This chemical is increasingly used as it is extracted from plant-based sources and considered ecologically safe. Cases of allergic contact dermatitis to lauryl glucoside have been repeatedly reported worldwide since the early 2000s as it is used in a wide array of products.
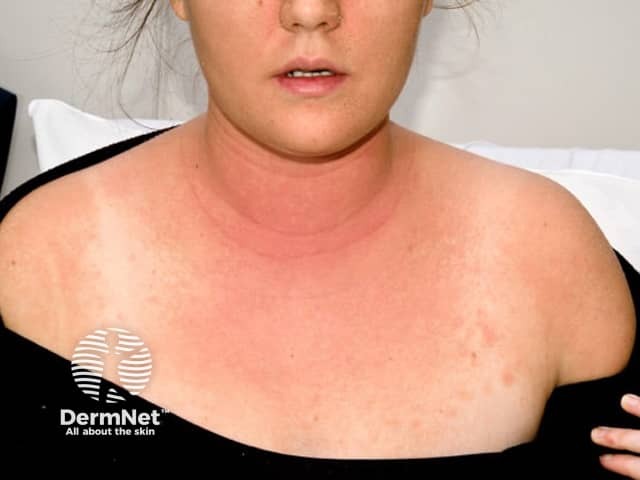
Contact allergy due to lauryl glucoside in a personal care product
Where is lauryl glucoside found?
Glucosides are used because of their emulsifying and foaming properties. For this property, lauryl glucoside may be found in:
It is also present in leave-on products such as:
- Sunscreens
- Deodorants
- Fragrances.
More recently, alkyl glucosides have been used in wound care products as well.
Who gets contact allergy to lauryl glucoside?
The true incidence of allergic contact dermatitis to lauryl glucoside is unknown but is reported to affect 0.7–2.0% of the patch-tested population. Women between the age of 40–50 years are more commonly affected.
Patients with an underlying history of eczema and atopy are at higher risk and some may also have contact allergies to other substances.
The most common source of allergy is from personal care products, in particular hair products and skin cleansers. For this reason, some occupations can lead to increased exposure and risk of allergy, for example, hairdressing and cleaning.
What are the features of contact allergy to lauryl glucoside?
- Localised redness, itching, swelling, or blistering hours to days after contact with a topical product containing lauryl glucoside.
- Lauryl glucoside can also cause irritant contact dermatitis and contact urticaria.
How is contact allergy to lauryl glucoside diagnosed?
Contact allergy is diagnosed by a dermatologist by patch testing. During the test, dilute allergens are placed on the skin for two days. At subsequent appointments, a specialist examines the skin and grades the level of reaction.
What is the patch testing concentration and vehicle for lauryl glucoside?
The patch testing concentration of lauryl glucosides (lauryl polyglucose) is 3% in petrolatum. An allergy to one alkyl glucoside can cause cross-reactivity to other glucosides and therefore, if there is a high suspicion of contact allergy to a specific glucoside, this needs to be tested separately. Testing for glucosides can be done using the cosmetic series for patch testing.
How is contact allergy to lauryl glucoside treated?
Avoidance of the allergen is the cornerstone of treatment of contact allergy. Patients are advised to check labels and meticulously screen for the allergen when purchasing products for individual use.
Bibliography
- Bhoyrul B, Solman L, Kirk S, et al. Patch testing with alkyl glucosides: Concomitant reactions are common but not ubiquitous. Contact Dermatitis. 2019;80(5):286–290. doi: 10.1111/cod.13186. Abstract
- Loranger C, Alfalah M, Le Bouedec MCF, & Sasseville D. Alkyl glucosides in contact dermatitis. Dermatitis. 2017;28(1):5–13. doi: 10.1097/DER.0000000000000240. Journal
- Soriano LF, Bertram CG, Chowdhury MMU, et al. Prevalence of allergic contact dermatitis to decyl and lauryl glucoside in the UK and Ireland. Br J Dermatol. 2021;184(3):571–573. doi: 10.1111/bjd.19603. Journal
- Severin RK, Belsito DV. Patch testing with decyl and lauryl glucoside: how well does one screen for contact allergic reactions to the other? Dermatitis. 2017;28(6):342–345. Journal
- Warshaw EM, Xiong M, Atwater AR, et al. Patch testing with glucosides: The North American Contact Dermatitis Group experience, 2009-2018. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2022;87(5):1033–1041. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2022.04.058. Journal
On DermNet
- Contact reactions to cosmetics
- Contact allergens
- Allergic contact dermatitis
- Irritant contact dermatitis
- Patch tests
- Baseline series of patch test allergens
Other websites
- Allergy New Zealand
- American Contact Dermatitis Society
- Patch testing for lauryl glycoside — patient information sheet
Books about skin diseases
