Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
What is melanoma? An introduction — extra information
What is melanoma? An introduction
Author: Vanessa Ngan, Staff Writer; Copy Editor: Clare Morrison; Chief Editor: Dr Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, October 2013. About Melanoma is sponsored by the New Zealand Dermatological Society Incorporated.
Introduction
More about melanocytes and melanin
Different types of melanoma
Melanoma types and sun damage
Rare types of melanoma
Primary and secondary melanoma
Melanoma is a skin cancer
- Melanoma (also called malignant melanoma) is a spot on the skin that contains cancer cells.
- Cancers are collections of cells that grow out of control and may invade surrounding tissues.
- Melanoma is a type of skin cancer that is sometimes dangerous because it can spread to other parts of the body and cause death.
- Melanoma grows from cells called melanocytes that have been damaged.
More about melanocytes and melanin
Melanocytes normally make a pigment called melanin.
- Normal melanocytes make melanin, which protects the skin from ultraviolet radiation (UVR) from the sun by absorbing it.
- Melanin is a brown-coloured pigment that determines our skin, eye and hair colour.
- Melanocytes do not make much melanin in people with fair skin, who are more likely to get melanoma.
- Melanocytes make more melanin in people with dark skin, who are thus less likely to get melanoma.
- Moles, also called melanocytic naevi, are due to nests of harmless melanocytes in the skin.
- People with lots of moles are prone to melanoma.
Some different skin types are shown below.
Skin burns. Does not tan
Skin burns easily. Tans poorly
Skin sometimes burns. Tans easily
Light brown skin. Rarely burns
Different types of melanoma
There are several different types of melanoma. The differences between them determine what a melanoma looks like, how quickly it will grow, where it appears on the body and who is most likely to get one.
Thin melanoma
Thin melanomas include:
-
Superficial spreading melanoma: most often found on trunk and limbs.
-
Lentigo maligna melanoma: found on scalp, face and neck.
-
Lentiginous melanoma: similar to lentigo maligna melanoma, but found on upper trunk and upper arms.
-
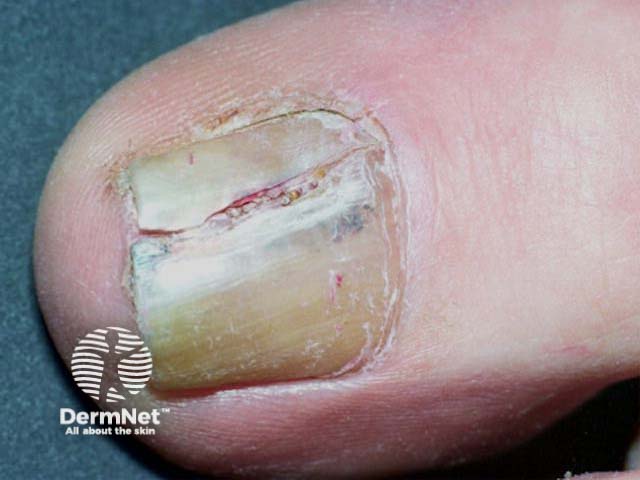
Acral lentiginous melanoma: much less common and found on palms, soles and under the nails.
-
A thin melanoma begins as a flat, multicoloured patch with a smooth surface. Colours may include light brown, dark brown, black, grey, blue, pink and white.
-
Cancer cells start growing "in situ" within the top layer of skin – this is called the horizontal growth phase.
-
This type of melanoma slowly grows bigger over months or years.
-
Eventually the melanoma invades into the deeper layers of skin – this is called the vertical growth phase.
-
Risk of spread to other tissues depends mainly on thickness of the melanoma at the time it is cut out.
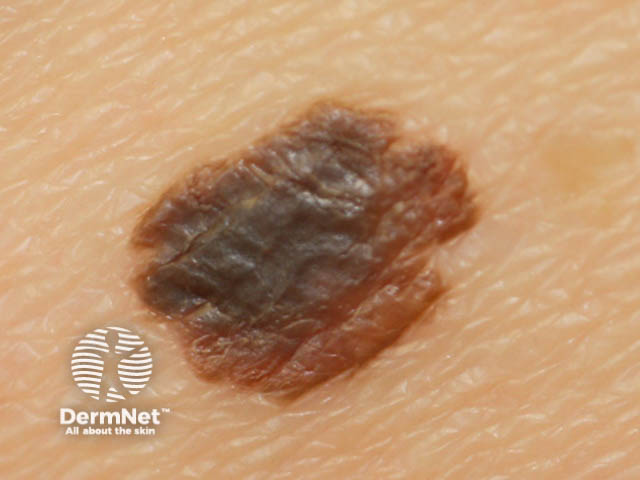
Superficial spreading melanoma
Lentigo maligna
Lentiginous melanoma
Acral lentiginous melanoma
- See more images of superficial spreading melanoma
- See more images of lentigo maligna melanoma
- See more images of acral lentiginous melanoma
Thick melanoma
Thick melanomas include:
-
Nodular melanoma: most often found on trunk and limbs.
-
Desmoplastic melanoma: rare, found on head and neck
-
Spitzoid melanoma: rare, but can affect children and young adults.
-
A thick melanoma appears as a raised lump that is often a red, black, or blue colour.
-
Cancer cells start growing in the deeper layers of skin.
-
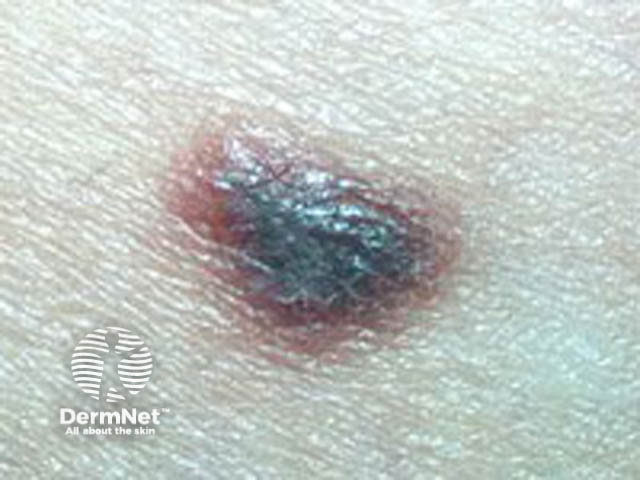
Red melanomas are called amelanotic melanomas.
-
Melanoma can grow rapidly over weeks to months, spreading upwards into the epidermis and downwards into subcutaneous tissue.
-
Early spread to other tissues (metastasis) may occur even before the melanoma has been surgically removed.
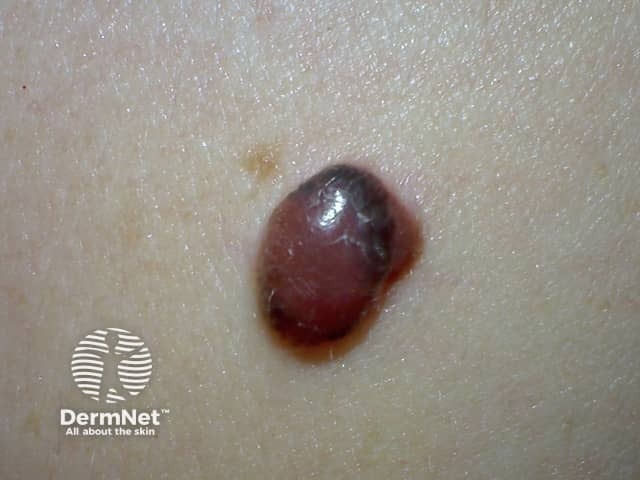
Nodular melanoma
Amelanotic nodular melanoma
Spitzoid melanoma
Desmoplastic melanoma
See more images of nodular melanoma
How do melanoma types relate to sun damage?
The behaviours of different types of melanoma vary according to the melanomas’ relationship to sun damage.
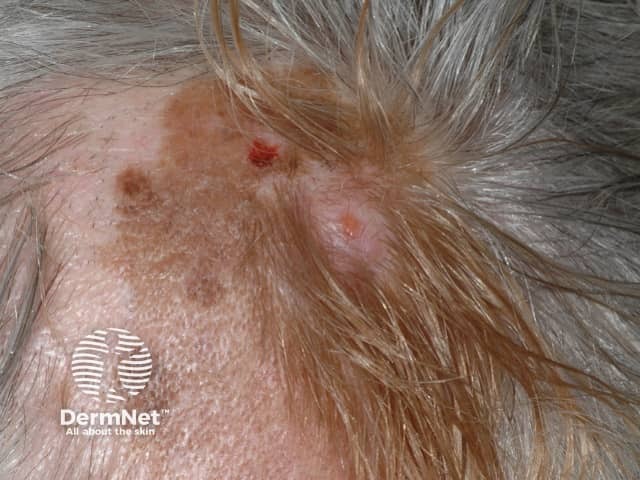
Chronic sun exposure
In New Zealand, melanoma often affects people who are sun damaged. This type of melanoma:
- Tends to affect older individuals.
- Is more common in men.
- Often occurs on the head and neck.
- May result in several melanomas.
- Usually occurs in people who have been exposed to the sun over a long period of time. These are often people that work outdoors, such as builders, farmers and gardeners.
- Is often a clinical type called lentigo maligna melanoma.
- Tends to be slow-growing and thin at diagnosis.
Intermediate sun exposure
Melanoma can also affect people who actually don't spend a lot of time outdoors. This type of melanoma is associated with earlier sunburn, and:
- Tends to affect younger adults.
- Is more common in women.
- Often affects fair-skinned people who have lots of moles.
- Most often occurs on the trunk of males and on the legs of females.
- Usually occurs in people who have been exposed to lots of sun occasionally, for example during sunny holidays spent sun-bathing or sailing.
- Is often a clinical type called superficial spreading melanoma.
- Can affect several members of one family, who have a genetic tendency to large and odd-looking (atypical) moles as well as melanoma.
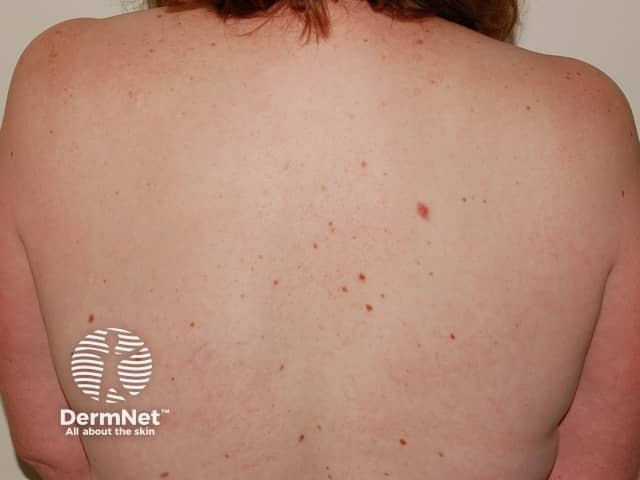
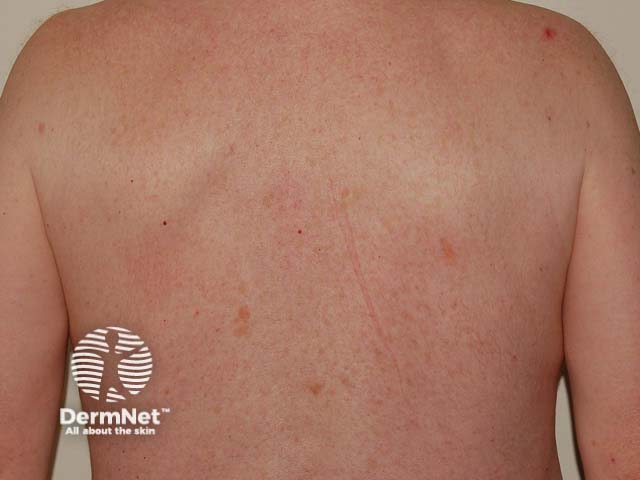
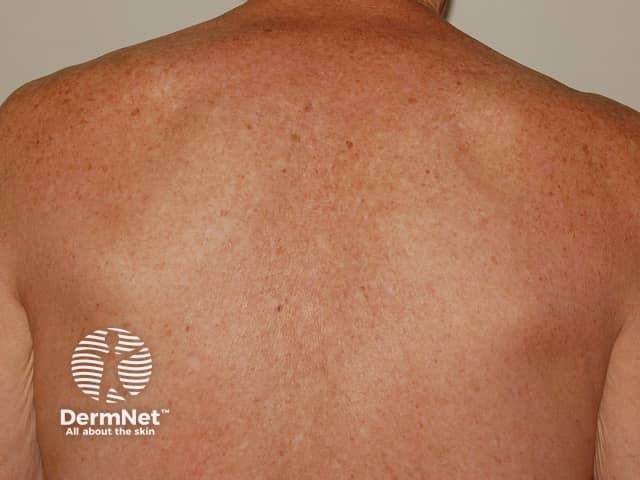
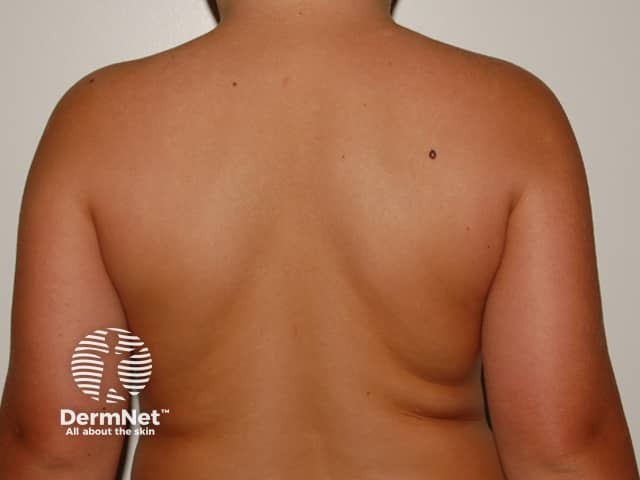
Differences in melanomas due to sun damage* and genetic predisposition**
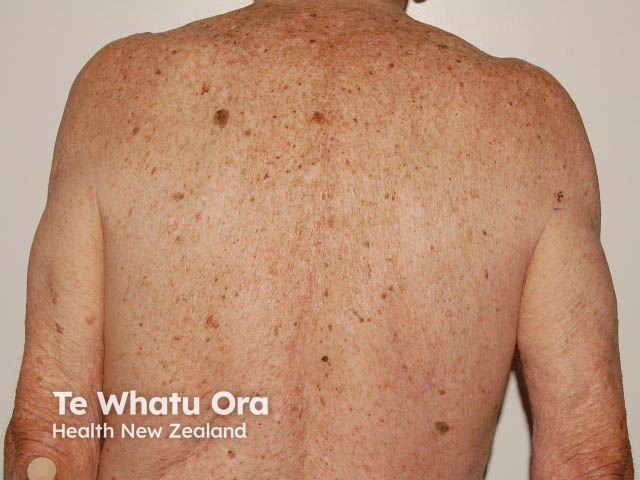
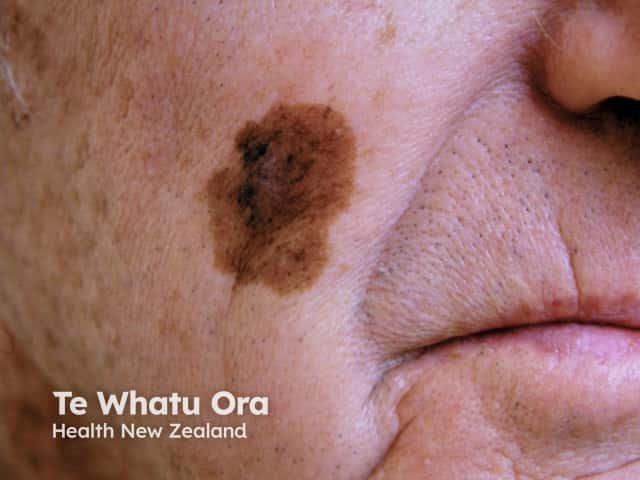
Chronic sun damage*
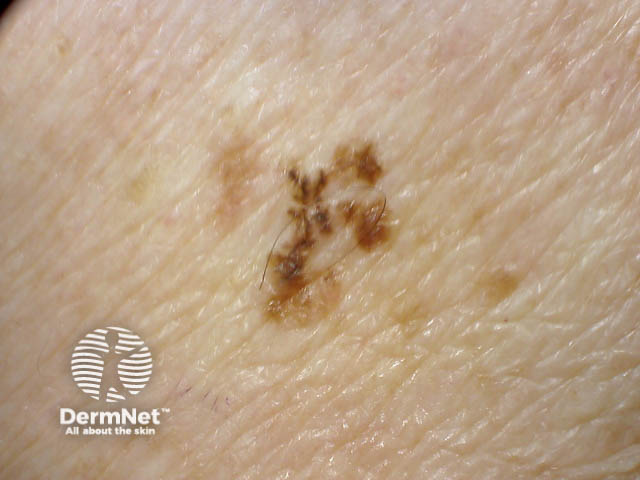
Close-up of melanoma*
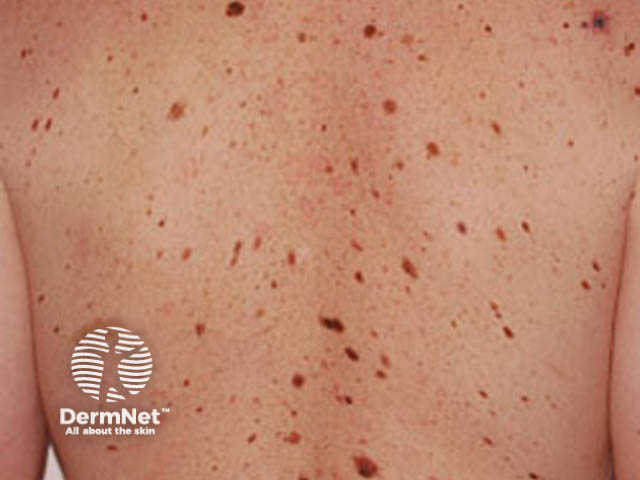
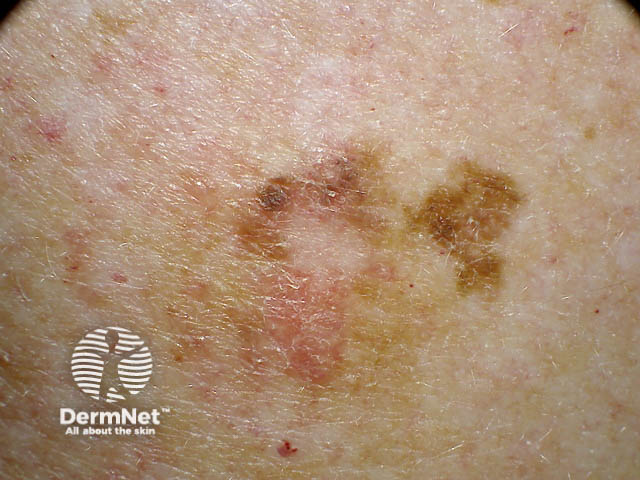
Many and unusual moles**
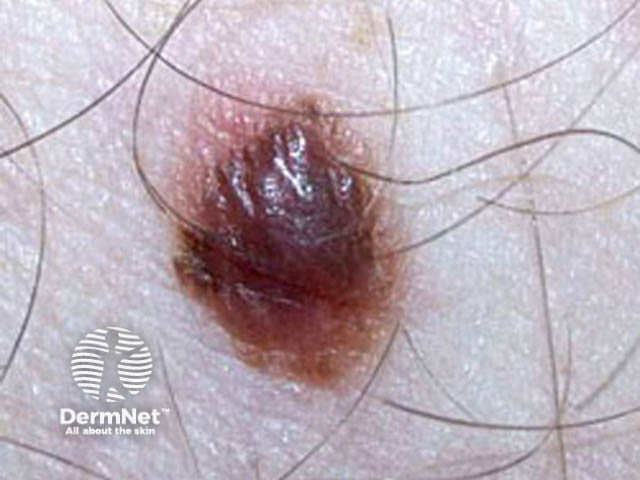
Close-up of melanoma**
Rare types of melanoma
Melanoma unrelated to sun exposure
Even people with very little exposure to the sun can get melanoma. Melanoma that is not associated with sun exposure:
- Includes rare and aggressive forms of melanoma.
- Is found at equal rates in people of all skin types.
- Includes some forms of nodular melanoma, mucosal melanoma and acral lentiginous melanoma.
- May grow quickly and is often thick at the time of diagnosis.
Melanoma that starts in other parts of the body is much less common than melanoma that starts in the skin. These types of melanoma can grow quickly and are sometimes hard to diagnose.
Mucosal melanoma
Mucosal melanoma starts within a mucous membrane. These are the moist linings that cover body cavities and passages such as the mouth, nose and eyelids, and urinary and genital tracts.
- Conjunctival melanoma grows on the surface of the eye.
- Oropharyngeal melanoma grows within the nasal sinuses, mouth or on the lips.
- Anogenital melanoma grows on the vulva, penis or anus.
Non-cutaneous melanoma
Melanoma may rarely start growing in melanocytes within the eye (uveal melanoma), the brain or spinal cord, the lymph glands, or elsewhere.
Primary and secondary melanoma
Melanoma is often described as primary or secondary.
Primary melanoma
Primary melanoma is the first sign of melanoma. It starts invisibly small within the skin (or rarely within another tissue) and grows over weeks to years.
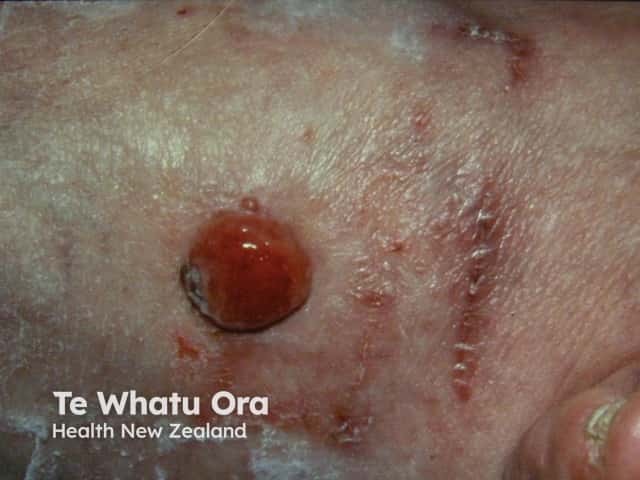
Nodular melanoma
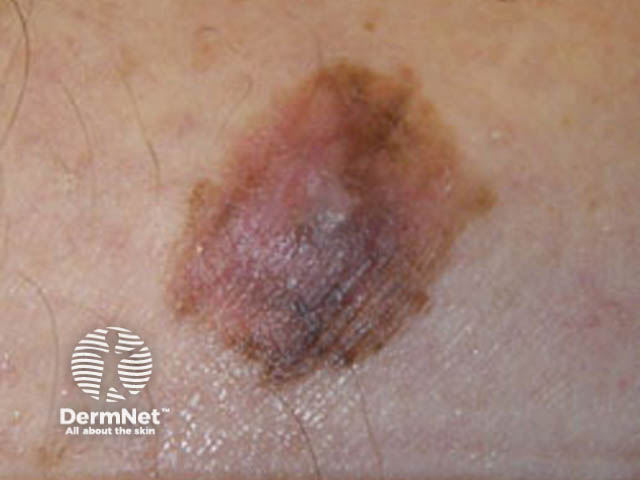
Superficial spreading melanoma
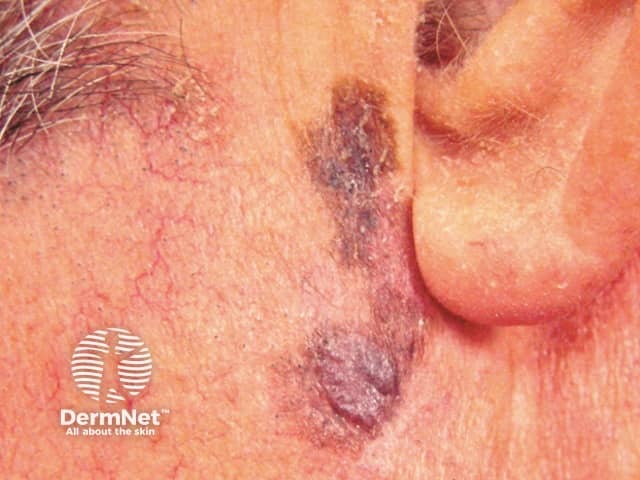
Lentigo maligna
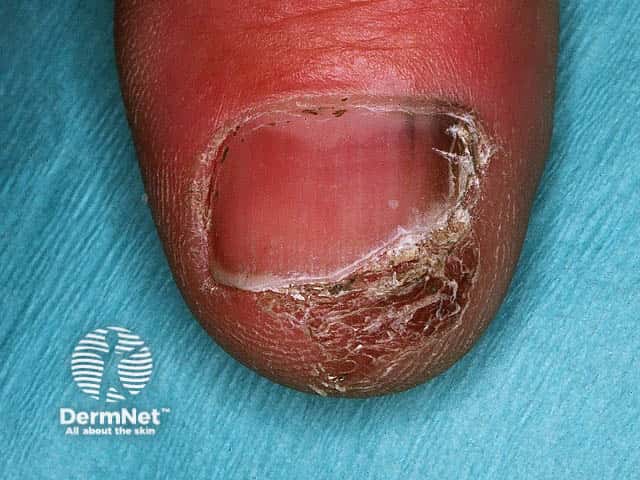
Nail melanoma
- See more images of nodular melanoma
- See more images of superficial spreading melanoma
- See more images of lentigo maligna melanoma
Secondary melanoma
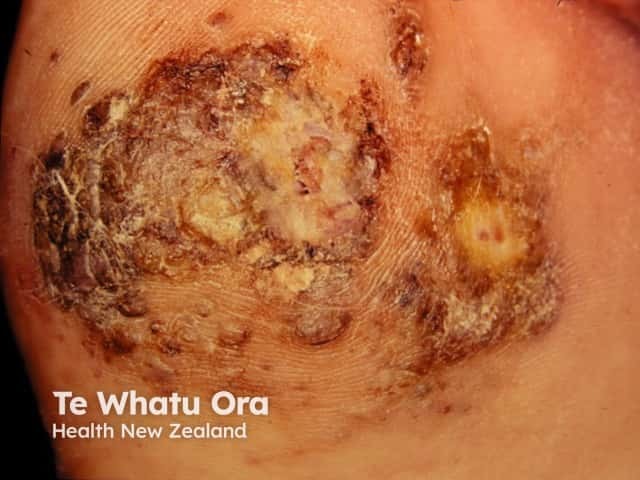
Secondary melanoma is the sign that melanoma has spread to other tissues. This is also called advanced melanoma or metastatic melanoma. Secondary melanoma tends to grow quickly (often noticeable over several weeks).
Deposits of metastatic melanoma may grow within lymph nodes (glands) in the neck, armpit or groin. They may also grow within the skin, brain, lungs, liver or other organs.
In about 3% of patients presenting with secondary melanoma (metastasis), the primary tumour is never found.
Metastatic melanoma is detected clinically on examination or by PET-CT scan.
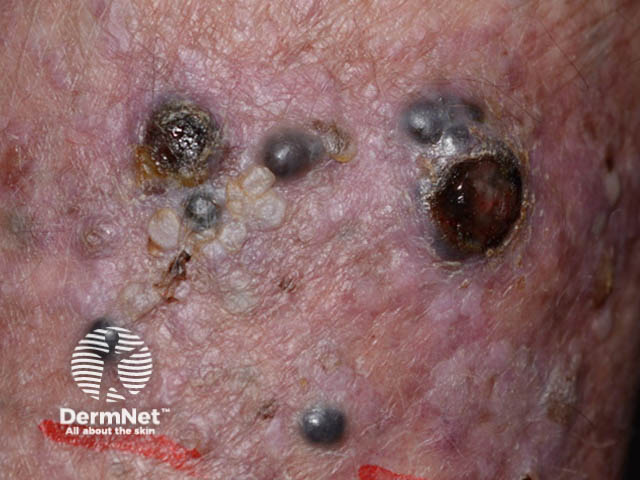
Secondary melanoma in the skin
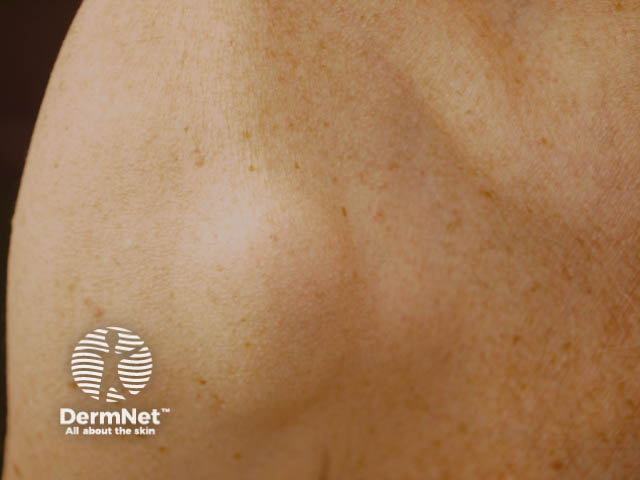
Melanoma under the skin
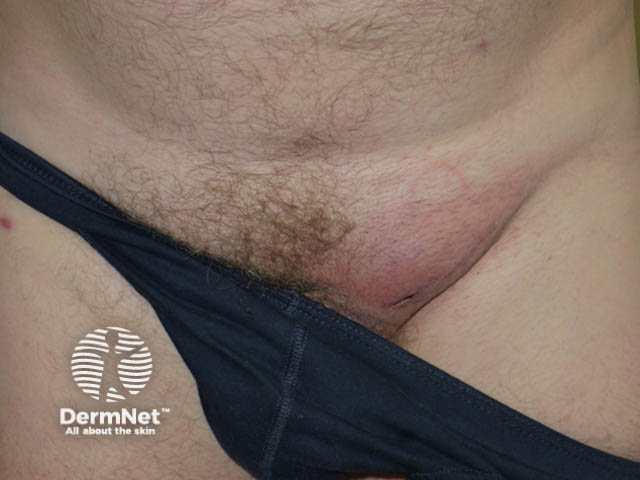
Melanoma in lymph glands
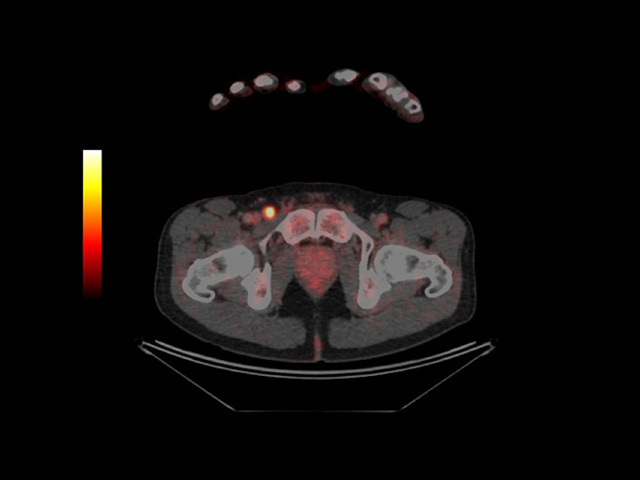
PET-CT scan: metastasis glows in groin
Next: Who gets melanoma?
On DermNet
- About melanoma: What is melanoma?| Who gets melanoma? | What causes melanoma?
- Stopping melanoma: Ban the tan! | Clothes count | Slap it on! | Is any sun good for me?
- Finding melanoma: Spot the difference! | Check your skin today | See your doctor | Do I have melanoma?
- Treating melanoma: Pathological diagnosis | How is melanoma removed? | Has my melanoma spread? | I have advanced melanoma: what now?
- Follow-up: Surviving melanoma | What's my outlook? | Clinical trials | Other resources
- Our melanoma videos
What is melanoma video (Dr Tina Tian).
