Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Wood lamp skin examination — extra information
Wood lamp skin examination
Author: A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. August 2014.
Introduction
Introduction - Wood lamp
How it works
Introduction - fluorescence
Condition diagnosed
Other uses
Safety
What is Wood lamp skin examination?
Wood lamp examination is a diagnostic test in which the skin or hair is examined while exposed to the black light emitted by Wood lamp. Blacklight is invisible to the naked eye because it is in the ultraviolet spectrum, with a wavelength just shorter than the colour violet. The lamp glows violet in a dark environment because it also emits some light in the violet part of the electromagnetic spectrum.
What is a Wood lamp?
A traditional Wood lamp is a low-output mercury arc covered by a Wood filter (barium silicate and 9% nickel oxide) and emits wavelength 320–450 nm (peak 365 nm). The lamp was invented in 1903 by a Baltimore physicist, Robert W. Wood.
Modern black light sources may be specially designed BLB fluorescent lamps, mercury vapour lamps, light-emitting diodes, or incandescent lamps. Fluorescent black light tubes have a dark blue filter coating on the tube, which filters out most visible light. There are several models with varying properties. The medical Wood lamp may include:
- A variety phosphors with different peak emission
- Magnifying lens
- White light
- Black drape to exclude light
Describe a Wood lamp skin examination
Examination using Wood lamp involves the following steps.
- Ideally, skin to be examined should not have been recently washed or had any makeup, deodorant or moisturising cream applied, as these can fluorescence causing a false positive result
-
- Gentle facial skin cleansing may be required
- The Wood lamp is turned on to warm up for about a minute
- Room lights are turned off, and window shades are drawn, or black drape used to darken the surroundings completely
- After waiting to adapt to the dark, the skin is examined with Wood lamp for a few seconds. The lamp is held about 10-30 cm away from the skin. The examination is painless and safe.
A Wood lamp is used to identify the extent of pigmented or depigmented patches and to detect fluorescence. Normal healthy skin is slightly blue but shows white spots where there is thickened skin, yellow where it is oily, and purple spots where it is dehydrated. Clothing lint often shines bright white.
A positive result is reported if a pigmentary disorder is more noticeable when examined using the Wood lamp or if fluorescence is noted.
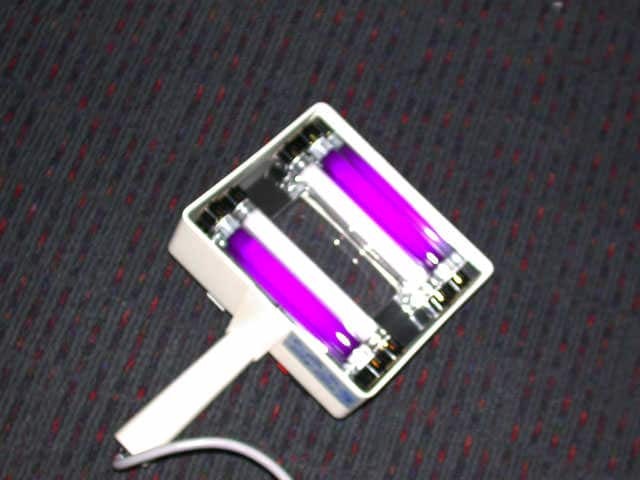

Burton Wood lamp
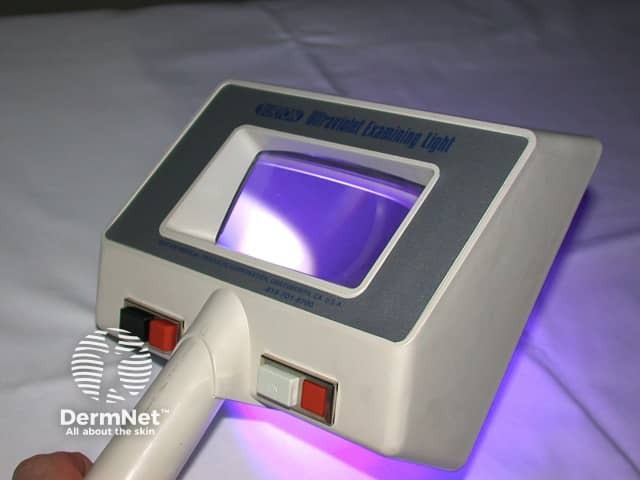

Wood lamp
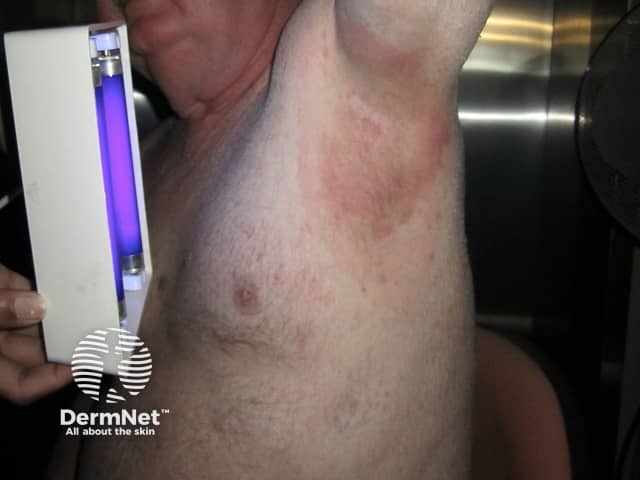
Wood lamp examination
What is fluorescence?
Fluorescence is a coloured glow seen when certain substances such as collagen and porphyrins absorb black light and emit it again at a longer wavelength in the visible spectrum. Items on the skin surface such as fabric, topical medications and soap residue can also fluoresce.
What conditions are diagnosed using a Wood lamp?
A Wood lamp for skin examination may reveal:
- Increase in pigmentation (eg, melasma, postinflammatory pigmentation) to determine whether the pigmentation is epidermal (pigmentation enhanced by Wood lamp examination) or dermal (pigmentation unchanged by Wood lamp examination). Pigmented lesions have a clear border under Wood light because the light is absorbed by increased melanin
- Loss of pigmentation (eg, vitiligo) or reduced pigmentation (eg, ash-leaf macules in tuberous sclerosis and hypomelanosis of Ito) to identify affected areas in light-skinned people. Hypopigmented skin has sharper borders under black light and fluoresces bright blue-white (or sometimes, yellowish green) due to accumulated biopterins. In contrast, areas of reduced blood flow are unchanged
- Pityriasis versicolor—a slightly scaly persistent rash on anterior chest and back caused by Malassezia yeasts. When active, the scale emits a yellowish or orange glow
- Malassezia folliculitis—hair follicles fluoresce bluish-white
- Tinea capitis—areas of scale and baldness due to fungal infection. Microsporum species fluoresce blue-green (M canis, M audouinii, M ferrugineum, M distortum); Trichophyton schoenleinii fluoresces dull blue. Fungal infection due to other organisms does not fluoresce
- Head lice and scabies
- Erythrasma—corynebacteria bacteria cause a pigmented rash in skin folds that fluoresces a coral-pink colour
- Pseudomonas in spa pool folliculitis and wound infection fluoresces green
- Acne fluoresces orange-red due to cutibacteria in hair follicles
- Porphyria causes red-pink fluorescence of the skin (porphyria cutanea tarda), or teeth (erythropoetic porphyria)
- Porphyrins used as the photosensitiser in photodynamic therapy
- Drugs on the skin surface—tetracyclines and mepacrine fluoresce after oral ingestion
- The evenness of application of a salicylic acid-containing chemical peel (this fluoresces green).
Fluorescence noted during Wood lamp examination

Coral-pink fluorescence in erythrasma using Wood lamp
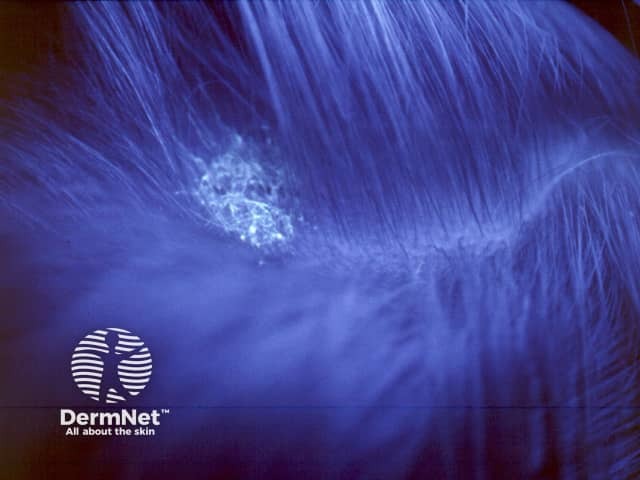

Fluorescence in tinea capitis using Wood lamp
Other uses for Wood lamp
Apart from Wood lamp skin examination, the Wood lamp has other uses.
- Biochemistry laboratory may look for signs of porphyria in red blood cells (erythropoietic protoporphyria), urine and stool (porphyria cutanea tarda)
- Molecular biology laboratory may use a Wood lamp to detect compounds with a fluorescent tag
- Aestheticians check for signs of ageing skin and other imperfections
- Ophthalmologists look for scratches and foreign bodies in the cornea of the eye
- Veterinary surgeons use the Wood lamp when examining pets for bacterial, fungal, or parasitic infection
- Law enforcement officers examine crime scenes and clothing for semen and urine
- Pet or rodent urine/faeces is easily detected using a Wood lamp
- Metal fatigue can be evaluated using a fluorescent fluid and Wood lamp examination
- Nightclubs use a Wood lamp to check fluorescent re-entry stamps
- Immigration officers check that passports are genuine
- Banks check for counterfeit money
- Mineralogy and gemology
- Displaying fluorescent paint used in art and sculpture
Does the Wood lamp cause any harm?
The black light emitted by a Wood lamp is harmless. The lamp does not emit short-wavelength ultraviolet B radiation (290–320 nm), so it does not cause sunburn or otherwise damage healthy skin.
It is possible that a patient with extreme photosensitivity might develop a rash on skin exposed to black light. However, Wood lamp examination is usually very brief and unlikely to cause problems even in very photosensitive patients.
It is prudent to ask the patient to close their eyes when examining the face.
References
- Wood's Lamp Examination — Georgia Department of Juvenile Justice
- Gupta LK, Singhi M K. Wood's lamp. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol [serial online] 2004 [cited 2014 Aug 8];70:131–5. Journal
On DermNet
Other websites
- Wood's lamp examination — MedlinePlus
- Black light — Wikipedia
