Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Verrucous haemangioma pathology — extra information
Verrucous haemangioma pathology
Author: Adjunct A/Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Clínica Ricardo Palma, Lima, Peru. DermNet Editor in Chief: Adjunct A/Prof Amanda Oakley. Copy edited by Gus Mitchell. September 2018.
Introduction
Histology
Special studies
Differential diagnoses
Introduction
Verrucous haemangioma (American spelling hemangioma) presents as blue-red, vascular papules, plaques, or nodules, which later become warty in appearance. These lesions do not resolve spontaneously and have a tendency to recur after excision if margins are inadequate.
Histology of verrucous haemangioma
In verrucous haemangioma, the histopathology shows irregular papillomatosis, acanthosis and hyperkeratosis of the epidermis. The dermis shows multiple, thin-walled, dilated blood-filled spaces. Intravascular thrombosis with recanalisation and haemorrhage can be seen (figures 1–5).
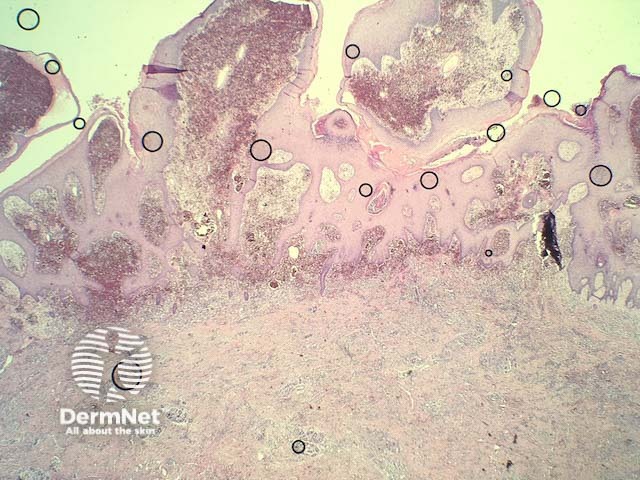
Figure 1
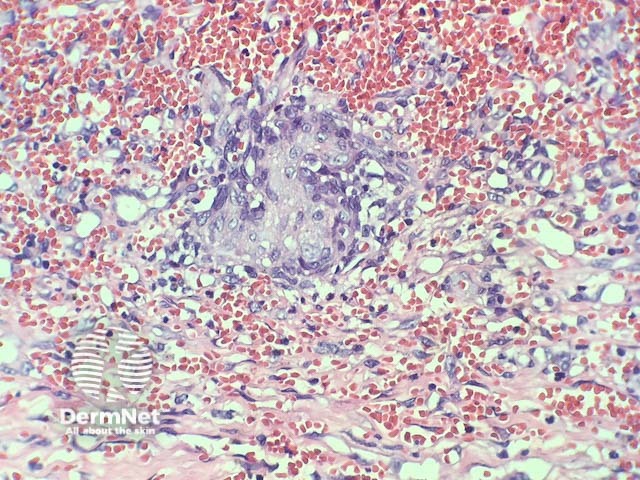
Figure 2
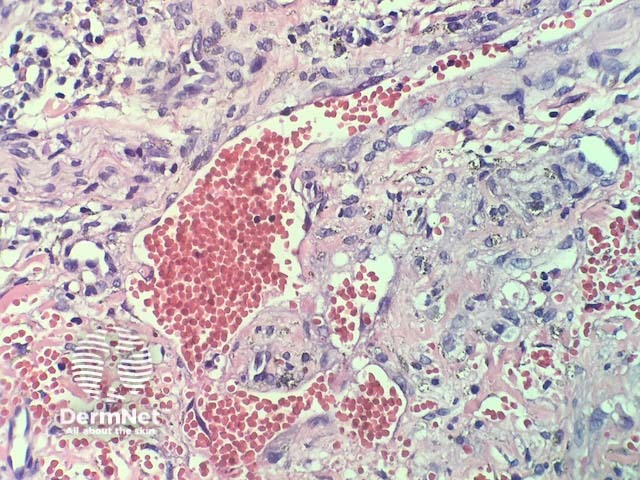
Figure 3
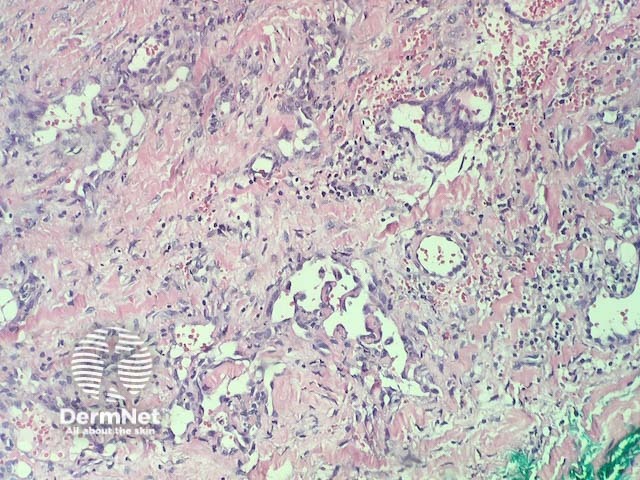
Figure 4
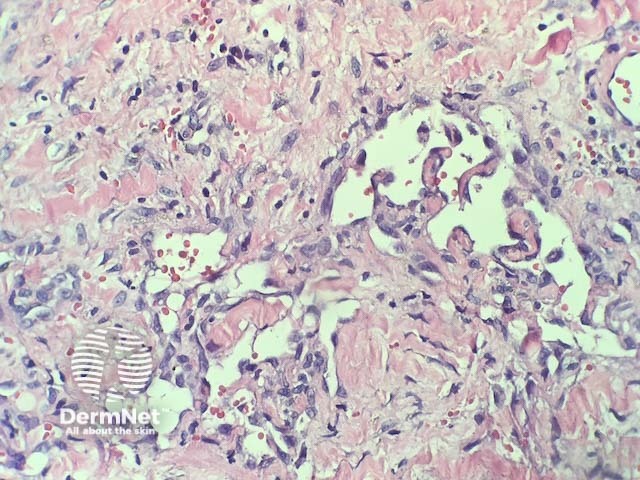
Figure 5
Special studies for verrucous haemangoma
Vascular markers can highlight the extent of the lesion (CD31, CD34).
Differential diagnosis for verrucous haemangioma
Other conditions that should be considered include:
- Angiokeratoma — these are generally smaller and are superficial. Involvement of the deep dermis and subcutis is not a feature of angiokeratoma
- Kaposi sarcoma — some areas of verrucous haemangioma can have infiltrative growth and mimic Kaposi sarcoma. Immunohistochemistry with HHV8 is negative in verrucous haemangioma.
References
- S Pavithra, H Mallya, H Kini, GS Pai. Verrucous hemangiona or angiokeratoma? A missed diagnosis. Indian J Dermatol 2011; 56: 599–600. doi: 10.4103/0019-5154.87171. PubMed Central
- Angiokeratoma. PathologyOutlines.com. Available at: http://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticangiokeratoma.html. Accessed 11 September 2018.
On DermNet
- Infantile haemangioma: Definition and pathogenesis
- Cherry angioma
- Vascular skin problems
- Skin lesions, tumours and cancers
- Dermatopathology glossary
- Dermatopathology index
