Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Pleomorphic hyalinising angiectatic tumour pathology — extra information
Lesions (cancerous) Diagnosis and testing
Pleomorphic hyalinising angiectatic tumour pathology
Author: Assoc Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand, 2013.
Pleomorphic-Hyalinising Angiectatic Tumour (PHAT) is a rare low-grade neoplasm which most commonly presents in adults as a slow-growing subcutaneous mass. As PHAT tends to be infiltrative, it is prone to local recurrence. Metastasis has never been reported.
There have been reports of PHAT recurring as overt sarcoma, but it is unclear whether these cases were misdiagnosed or whether evolution into overt sarcoma may occur.
Histology of Pleomorphic Hyalinising Angiectatic Tumour (PHAT)
Microscopically, PHAT is characterized by thin-walled, hyalinised and dilated blood vessels (figures 1, 2). Surrounding these is a stroma containing tumour cells which are plump spindled or ovoid cells with pleomorphic nuclei and occasional nuclear pseudoinclusions (Figures 2-3). Mitotic figures are rarely found. There may be extensive hemosiderin deposition (figure 3).
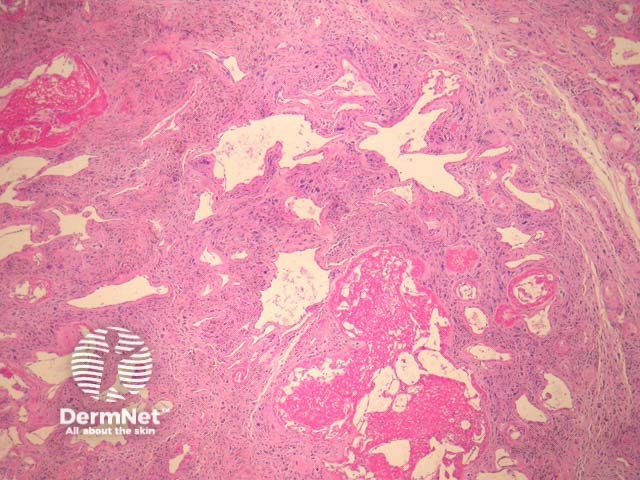
Figure 1
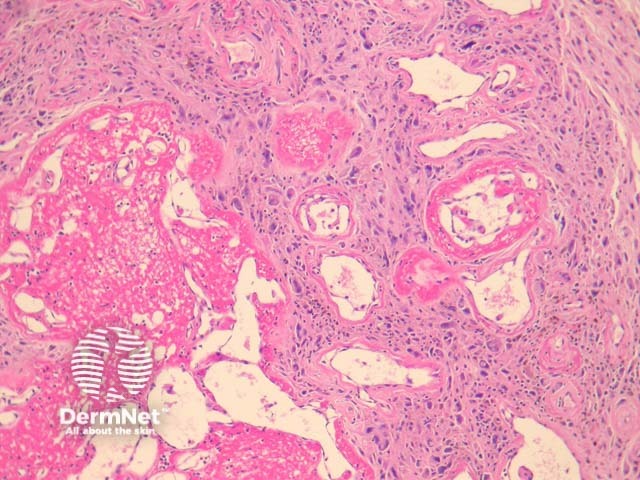
Figure 2
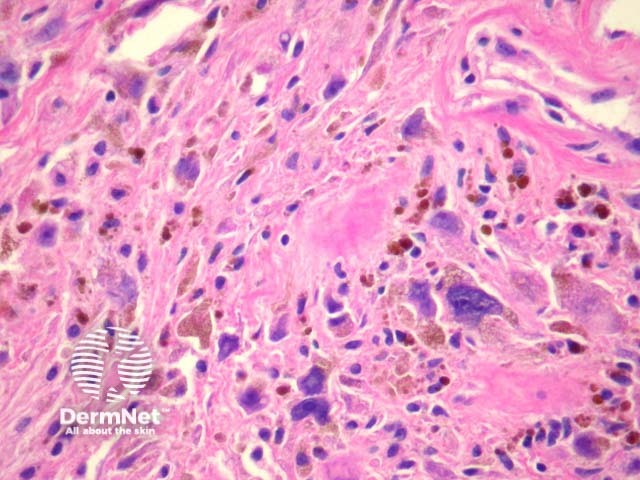
Figure 3
Special studies for Pleomorphic Hyalinising Angiectatic Tumour (PHAT)
Vimentin, CD34 and factor XIIIa may be positive in PHAT. There is no staining with S100 protein.
Differential diagnosis of Pleomorphic Hyalinising Angiectatic Tumour (PHAT) pathology
Schwannoma – These are S100 positive
Myxofibrosarcoma – These exhibit numerous mitoses. There have been reports of myxofibrosarcoma with areas suggestive of PHAT. If fully sampled, it is expected that such lesions should include classic areas of myxofibrosarcoma with a high proliferative index.
References
- Lewin MR, Montgomery EA, Barrett TL. New or unusual dermatopathology tumors: a review. J Cutan Pathol. 2011 Sep;38(9):689-96.
On DermNet
