Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Pityriasis rubra pilaris pathology — extra information
Pityriasis rubra pilaris pathology
Author: Assoc Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand, 2014.
Pityriasis rubra pilaris or PRP presents clinically as a papulosquamous eruption with follicular plugging and perifollicular erythema. The various clinical forms share the same histopathologic features.
Histology of pityriasis rubra pilaris
In PRP, the epidermis shows regular acanthosis and psoriasiform hyperplasia (figures 1-3). The horn is thickened with parakeratotic foci between orthokeratosis both vertically and horizontally (not seen clearly in the presented images). The hyperkeratosis tracks down the openings of follicular structures forming follicular plugs (figures 1-3). The dermis may contain a mixed sparse infiltrate which may be lichenoid. Rarely, foci of acantholysis may be seen (figure 3) and some authors have made associations with Darier disease.
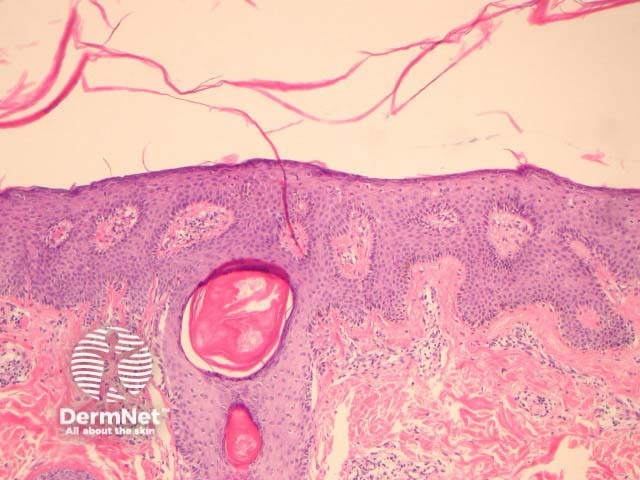
Figure 1
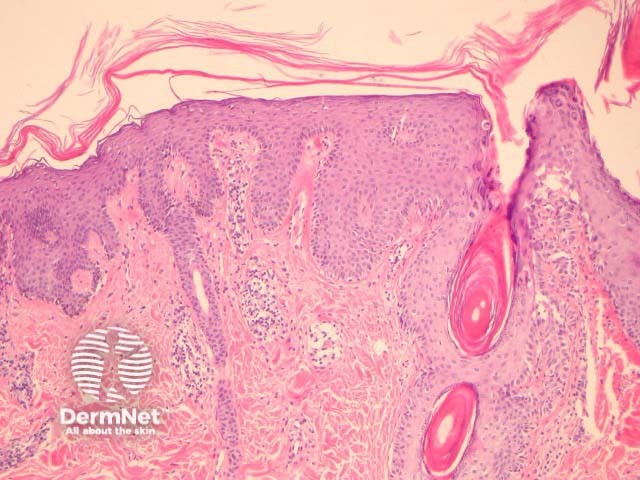
Figure 2
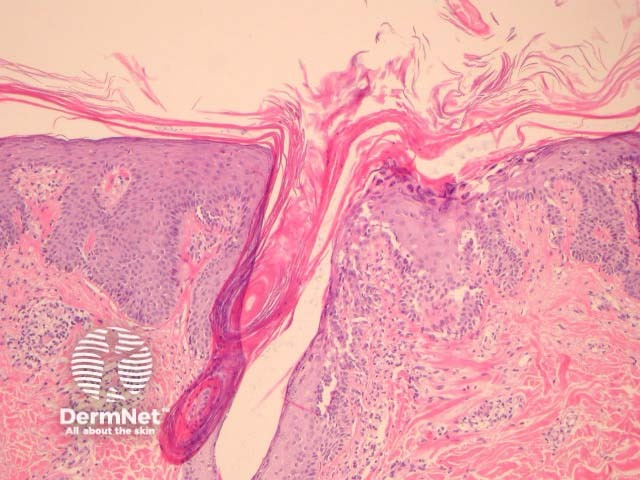
Figure 3
Special studies for pityriasis rubra pilaris
None are generally needed. PAS may be helpful to rule out fungal infections.
Differential diagnosis of pityriasis rubra pilaris
Psoriasis – Neutrophilic infiltrates and spongiform pustulation are clues to psoriasis.
Syphilis – Can be in the differential when there is a psoriasiform eruption with lichenoid features and plasma cells.
Mycosis fungoides – Mixed psoriasiform, spongiotic, and lichenoid patterns raise the possibility of mycosis fungoides or parapsoriasis.
References
- Weedon's Skin Pathology (Third edition, 2010). David Weedon
- Ko CJ, Milstone LM, Choi J, McNiff JM. Pityriasis rubra pilaris: the clinical context of acantholysis and other histologic features. Int J Dermatol. 2011 Dec;50(12):1480–5. PubMed
On DermNet
