Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Oral retinoids — extra information
Treatments Follicular disorder
Oral retinoids
Author: Dr Tim Aung, Primary Care Practitioner, Brisbane & Logan, Queensland, Australia. DermNet Editor in Chief: Adjunct A/Prof Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand. June 2020.
Introduction
How they work
Indications
Adverse effects
Uses
Interactions with other drugs
Monitoring
What are oral retinoids?
Retinoids are a group of medications related to vitamin A. They are used to treat various inflammatory skin disorders, skin cancer, and skin ageing.
Retinoids are classified into four generations [1,2,3]:
- 1st generation (non-aromatic retinoids): retinol, retinal, tretinoin (retinoic acid), isotretinoin, and alitretinoin
- 2nd generation (mono-aromatic retinoids): etretinate (withdrawn from the market) and its metabolite acitretin
- 3rd generation (poly-aromatic retinoids): adapalene, bexarotene, and tazarotene
- 4th generation retinoid: trifarotene.
Oral retinoids include:
- Acitretin
- Alitretinoin
- Bexarotene (a rexinoid)
- Isotretinoin
- Vitamin A (retinol).
How do retinoids work?
The effects of retinoids are mediated through binding to and activation of the retinoic acid receptor (RAR) and the retinoid X receptor (RXR), which regulate cell proliferation, differentiation and apoptosis [4,5]. They also have a role in immune modulation, are anti-inflammatory, and activate tumour suppressor genes.
What are the indications for oral retinoids?
The therapeutic use of retinoids depends on the individual product [6,7]. Their specific usage varies at the approval of individual country and on the results of off-label trials [1,4,8,9,10].
- Oral isotretinoin is approved for the treatment of acne. It is also used for other severe follicular conditions, such as rosacea, seborrhoea, hidradenitis suppurativa, and scalp folliculitis.
- Oral tretinoin is used for certain cancers (eg, acute promyelocytic leukaemia).
- The antiproliferative action of acitretin is useful for severe psoriasis (pustular psoriasis, erythrodermic psoriasis, and palmoplantar psoriasis) and other refractory skin disorders, such as palmoplantar keratoderma, pityriasis rubra pilaris, Darier disease, lichen planus, lichen sclerosus, and cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
- Bexarotene is used for cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
- Alitretinoin is approved for treatment-resistant chronic hand eczema.
Indications for an oral retinoid
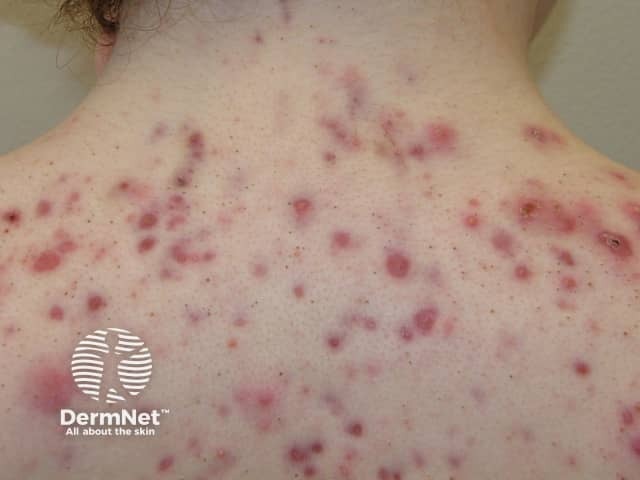
Severe acne
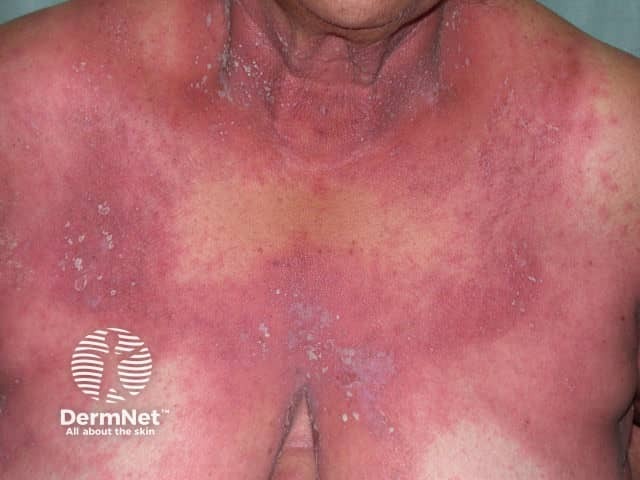
Generalised pustular psoriasis
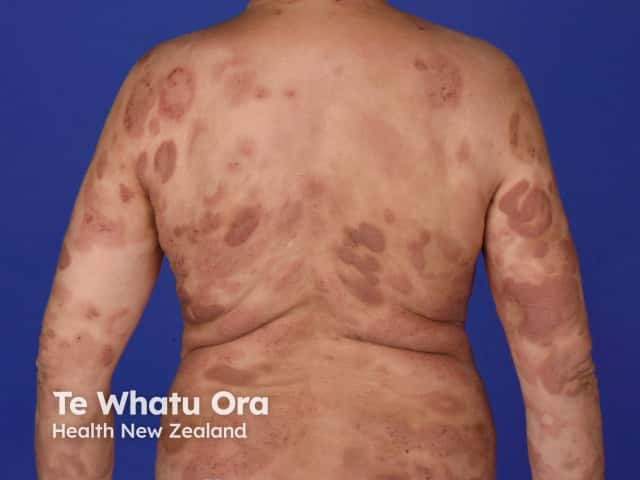
Cutaneous T-cell lymphoma
What are the adverse effects of oral retinoids?
The most serious adverse effect of oral retinoids is teratogenicity (category X) if a retinoid is taken during pregnancy. The most frequent birth malformations caused by oral retinoids are craniofacial, central nervous system, cardiovascular, and thymic [11].
Systemic treatment may also cause:
- Mucocutaneous effects: cheilitis, dryness of the oral mucosa, epistaxis, xerophthalmia, xerosis, fingertip fissuring, hair loss, nail fragility, periungual granuloma, paronychia
- Musculoskeletal effects: myalgia, arthralgia, bone pain, premature fusion of the epiphyses, skeletal hyperostosis, calcification of tendons and ligaments
- Neurological effects: headaches, raised intracranial pressure
- Ophthalmologic effects: nyctalopia (loss of night vision)
- Gastrointestinal/metabolic effects: nausea, abdominal pain, diarrhoea, elevated liver enzymes and lipids (triglycerides and cholesterol).
- Psychiatric effects: depression, irritability/aggression, suicidality, and sleep disturbances. Retinoid-associated depression and suicidality are debatable due to the lack of valid/scientific study.
How are oral retinoids used?
Follow the instructions carefully.
- Oral retinoids are taken after meals to maximise the absorption as they are lipid-soluble.
- Detailed dosage and treatment duration depend on the individual product and disease [4,6,9]
- Women of reproductive age must not take oral retinoid therapy unless effective contraception is established (eg, a long-acting reversible contraceptive). Contraception should be initiated one month before the start of treatment, after excluding pregnancy. It should continue after completion of treatment for at least two months for isotretinoin and 3 years for etretinate or acitretin [12]. Contraception is not required for male patients.
- Blood donation is not permitted in patients taking systemic retinoids.
What are the interactions or retinoids with other drugs?
Drug interactions with oral retinoids are uncommon and generally mild.
- Tetracycline may increase the risk of benign intracranial hypertension.
- Vitamin A supplementation could lead to hypervitaminosis.
- Methotrexate could cause hepatotoxicity so liver function tests should be monitored.
- Gemfibrozil, phenytoin, rifampicin, carbamazepine and ciprofloxacin increase bexarotene levels and its toxicity.
- Bexarotene reduces the effect of ciclosporin.
- Alcohol increases the conversion of acitretin to etretinate leading to hepatoxicity.
What monitoring should be undertaken on oral retinoids?
The effects of the oral retinoid and progress of the disease should be monitored at regular follow-up appointments.
- The workup before treatment includes a thorough history, physical examination and discussion about the pros and cons of the treatment.
- Initial laboratory tests include a pregnancy test (serum or urine) for female patients, complete blood count (CBC), lipid, renal and liver (LFT) profiles.
- Lipids, CBC, and LFT are typically repeated one month following the start of treatment, and then 3–6 monthly.
Approved datasheets are the official source of information for medicines, including approved uses, doses, and safety information. Check the individual datasheet in your country for information about medicines.
We suggest you refer to your national drug approval agency such as the Australian Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA), US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), UK Medicines and Healthcare products regulatory agency (MHRA) / emc, and NZ Medsafe, or a national or state-approved formulary eg, the New Zealand Formulary (NZF) and New Zealand Formulary for Children (NZFC) and the British National Formulary (BNF) and British National Formulary for Children (BNFC).
References
- Aryal A, Sabita Upreti S. A brief review on systemic retinoids. IJPSR, 2017; Vol. 8(9): 3630–9. doi: 10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.8(9).3630-39. Journal
- Aubert J, Piwnica D, Bertino B, Blanchet-Réthoré S, Carlavan I, Déret S, et al. Nonclinical and human pharmacology of the potent and selective topical retinoic acid receptor-γ agonist trifarotene. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug;179(2):442–56. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16719. PubMed
- Balak DMW. Topical trifarotene: a new retinoid. Br J Dermatol. 2018 Aug;179(2):231–2. doi: 10.1111/bjd.16733. PubMed
- Chien AL, Vahlquist A, Saurat J-H, Voorhees JJ, Kang S. Retinoids: pharmacology and mechanism of action. In: Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology-Vol 1+2_2020,9e. p3395–404.
- Bushue N, Wan YJ. Retinoid pathway and cancer therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2010 Oct 30;62(13):1285–98. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2010.07.003. Epub 2010 Aug 3.
- Khalil S, Bardawil T, Stephan C, Darwiche N, Abbas O, Kibbi AG, et al. Retinoids: a journey from the molecular structures and mechanisms of action to clinical uses in dermatology and adverse effects. J Dermatolog Treat. 2017 Dec;28(8):684–96. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2017.1309349. PubMed
- Scott LJ. Drugs. Trifarotene: First Approval. 2019 Nov;79(17):1905–9. doi: 10.1007/s40265-019-01218-6. PubMed
- Forbat E, Ali FR, Al-Niaimi F. Dermatological indications for the use of isotretinoin beyond acne. J Dermatolog Treat. 2018 Nov;29(7):698–705. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2018.1445194. PubMed
- Nickle SB, Peterson N, Peterson M. Updated Physician's Guide to the off-label uses of oral isotretinoin. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2014 Apr;7(4):22–34. PubMed
- Aung T, Rodins K. Persistently itchy papules. Aust J Gen Pract. 2019 May;48(5):286–8. doi: 10.31128/AJGP-07-18-4653. Journal
- Browne H, Mason G, Tang T. Retinoids and pregnancy: an update. The Obst&Gy, onlinetog.org; 2014;16:7–11. doi: 10.1111/tog.12075.
- European Medicines Agency (EMA). Retinoids containing medical products: update. Available at (https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/referral/retinoid-article-31-referral-annex-iii_en.pdf (accessed 26/01/2020).
On DermNet
