Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Gingivitis and periodontitis — extra information
Gingivitis and periodontitis
Author: Brian Wu PhD. MD Candidate, Keck School of Medicine, Los Angeles, USA; Chief Editor: Dr Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, November 2015.
Introduction Demographics Causes Clinical features Complications Diagnosis Treatment
What are gingivitis and periodontitis?
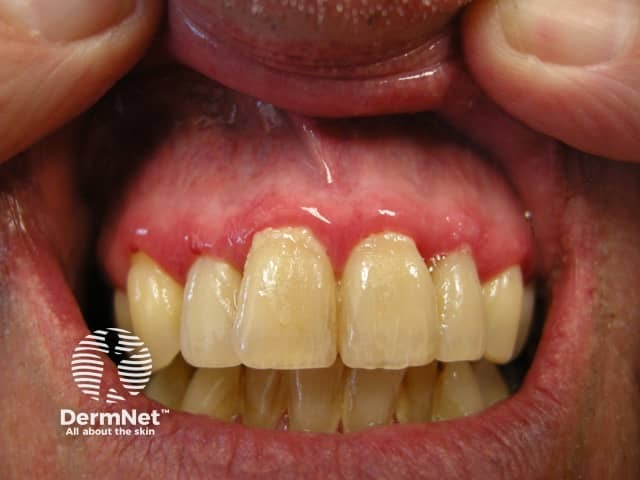
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums (gingiva), the visible mucosa around the teeth.
Periodontitis is a chronic, inflammatory disease affecting the gingiva, ligaments and the underlying alveolar bone.
Who gets gingivitis and periodontitis?
Risk factors for developing gingivitis and periodontitis include:
- Poor or inadequate oral hygiene practices
- Tobacco use
- Hereditary factors
- Immune compromise
- Viral and yeast infections
- Dry mouth
- Hormonal changes associated with menses and pregnancy
- Poor nutrition such as scurvy
- Substance abuse
- Ill-fitting dental restoration
- Type 1 diabetes, leukaemia, Down syndrome, Papillon-Lefevre syndrome and Crohn disease.
What causes gingivitis and periodontitis?
Gingivitis is caused by:
- The build-up of plaque if teeth are not cared for properly hardens into tartar and irritates the gingiva
- Systemic disorders such as diabetes or leukaemia predispose to oral infection
- Exposure to heavy metals, pellagra (niacin deficiency) and scurvy (Vitamin C deficiency) affect the integrity of the mucosa
- Skin disease, particularly erosive lichen planus of the mouth damages the mucosa resulting in inflammation and secondary infection of the gums.
The build-up of tartar leads to periodontitis. The tartar irritates the gingiva and forms pockets that fill with bacteria, plaque and tartar. Subsequent infection can be serious.
What are the clinical features of gingivitis and periodontitis?
Patients with gingivitis present with:
- Puffy, dusky red, swollen gums
- Gums which are tender and bleed easily
- Foul breath.
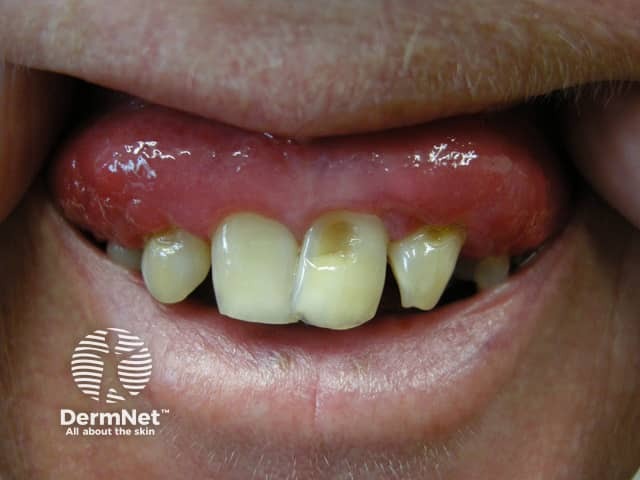
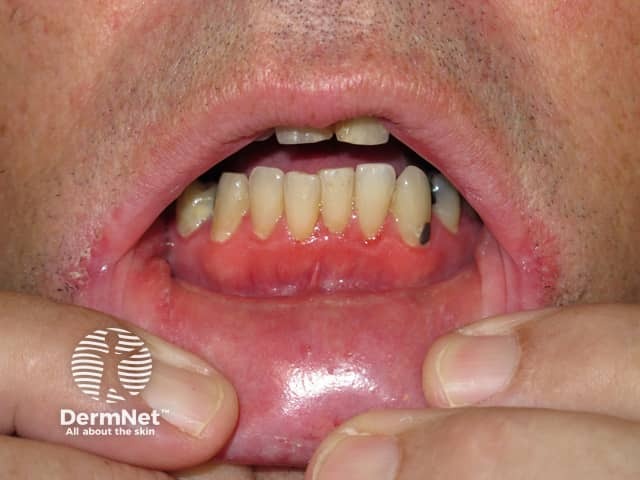
Patients with the more advanced periodontitis may present with:
- Swollen, tender, receding bright red or purplish gums
- New spaces between the teeth
- Foul breath
- Pus between the teeth and the gums
- Loose teeth.
Gingivitis
What are the complications of gingivitis and periodontitis?
The main complication of untreated gingivitis is periodontitis. Complications stemming from periodontitis include:
- Soft tissue damage in the mouth
- Tooth loss
- Destruction of alveolar bone
- Increased risk for coronary artery disease
- Increased risk for diabetes
- Increased risk for respiratory diseases like asthma
- Increased risk for rheumatoid arthritis
The link between periodontitis and increased risk of these serious chronic conditions is not fully understood.
How are gingivitis and periodontitis diagnosed?
Diagnosis for gingivitis and periodontitis is based upon thorough examination of the patient’s mouth, including cheeks, gums, and tongue. Probes may be used to examine gingival pockets.
X-rays may also be taken to evaluate possible damage to underlying bone structures.
How are gingivitis and periodontitis treated?
Treatment for gingivitis includes:
- Thorough teeth cleaning (descaling) to remove plaque and tartar
- At-home care includes brushing at least twice a day with a soft-bristled brush, use of mouthwash and dental floss
- Regular dental checkups
- Treatment of underlying conditions
Additional treatment for periodontitis includes:
- Root planning to remove build-up from the roots of the teeth
- Oral antibiotics to treat infection
- Flap surgery
- Soft tissue grafts
- Bone grafts
- Guided tissue restoration
References
- Gingivitis. Mayo Clinic. 2015
- Periodontitis. Mayo Clinic. 2015.
- Ubertallli, J. Gingivitis. Merck Manual Professional Edition. 2015.
- Ubertalli, J. Periodontitis. Merck Manual Professional Edition. 2015.
On DermNet
Other websites
- Gingivitis — Medscape Reference
- Gingivitis — Merck Manual Consumer Version. 2015.
- Periodontitis — Merck Manual Consumer Version. 2015.
