Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Dermoid cyst pathology — extra information
Lesions (benign) Diagnosis and testing
Dermoid cyst pathology
Author: Assoc Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand, 2013.
Introduction Histology Special studies Differential diagnosis
Introduction
Dermoid cysts are derived from the ectoderm and involve embryologic closure lines.
Histology of dermoid cyst
Sections show a subcutaneous cyst which is often received 'shelled out' (figure 1).
The lining is typically a keratinising squamous epithelium (figures 2, 3). The hallmark of these cysts is the presence of pilosebaceous structures in the cyst wall (figures 2, 3). Hair shafts are often found within the cyst (figure 3, arrow).
Less common findings include a columnar or mucus-secreting epithelium, smooth muscle in the cyst wall, and surrounding eccrine glands.
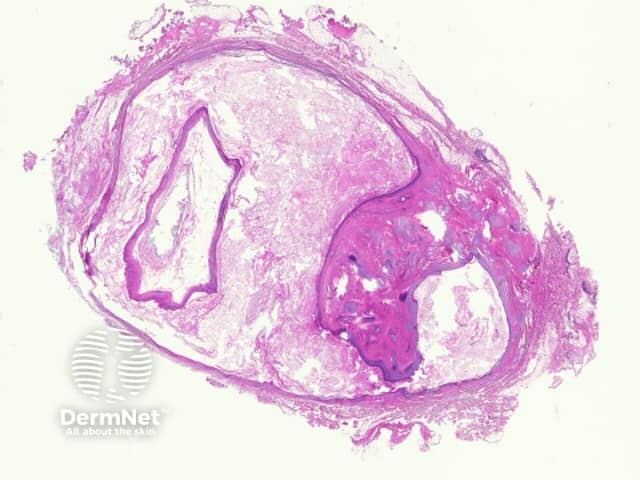
Figure 1
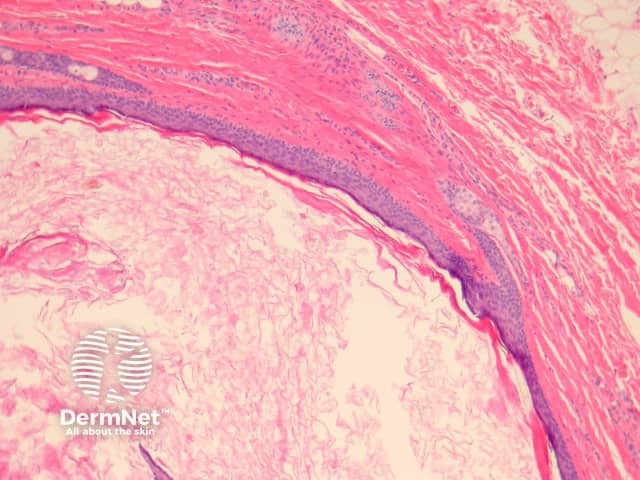
Figure 2
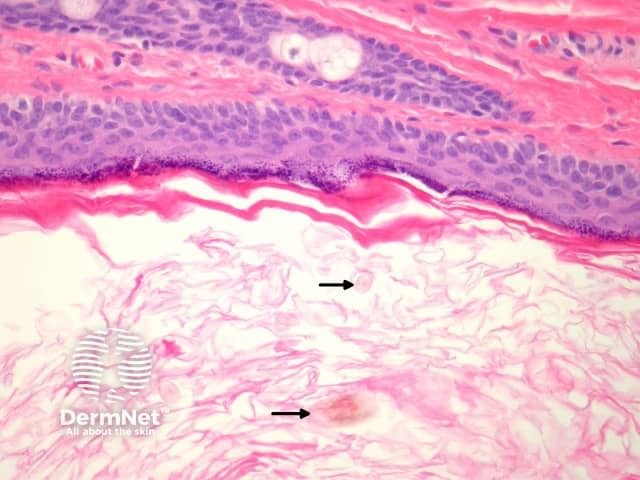
Figure 3
Special studies for dermoid cyst
None are needed.
Differential diagnosis of dermoid cyst pathology
Steatocystoma — steatocystoma shows sebaceous glands connecting to the cyst lining but the pilar structures are not seen. The lining lacks a granular layer and has a characteristic corrugated keratin layer.
References
- Weedon’s Skin Pathology (Third edition, 2010). David Weedon
On DermNet
- Dermoid cyst
- Choristoma
- Dermatopathology glossary
- Cutaneous cysts and pseudocysts
- Dermatopathology index
Books about skin diseases
