Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Dermatomyofibroma pathology — extra information
Lesions (benign) Diagnosis and testing
Dermatomyofibroma pathology
Author: Assoc Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand, 2013.
Introduction Histology Special studies Differential diagnoses
Introduction
Dermatomyofibroma was first described as a plaque-like dermal fibromatosis. It is a rare but distinct benign dermal proliferation of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in the dermis.
Histology of dermatomyofibroma
Sections show a subtle, ill-defined, plaque-like dermal proliferation (figure 1). The cells are uniform, slender, spindle-shaped and bland. The cells contain evenly distributed chromatin or vesicular with small nucleoli and indentations is in keeping with a myofibroblastic line of differentiation. Characteristically, the cells are arranged parallel to the epidermis (figures 2, 3).
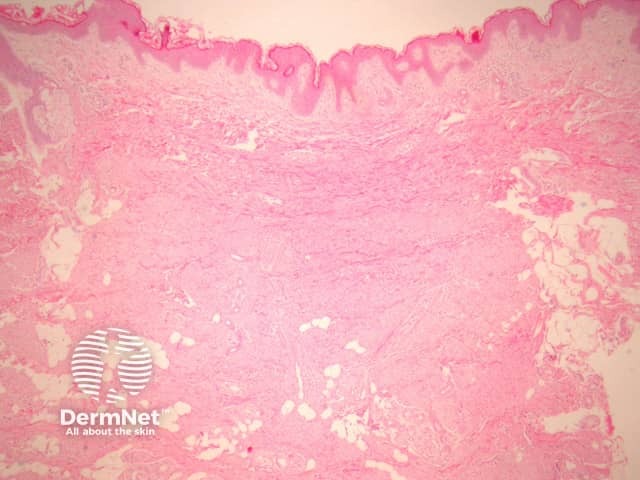
Figure 1
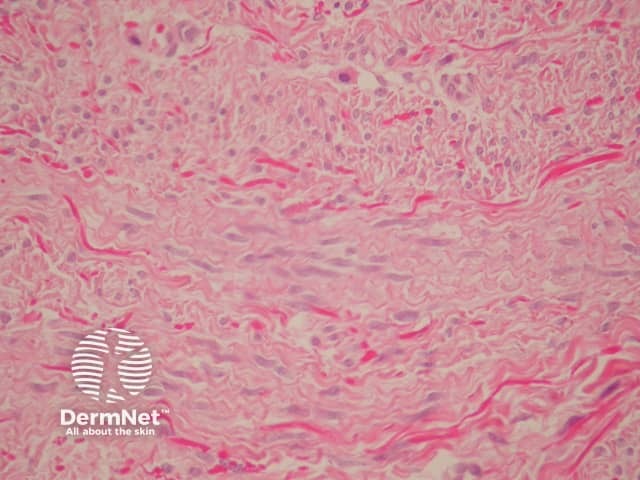
Figure 2
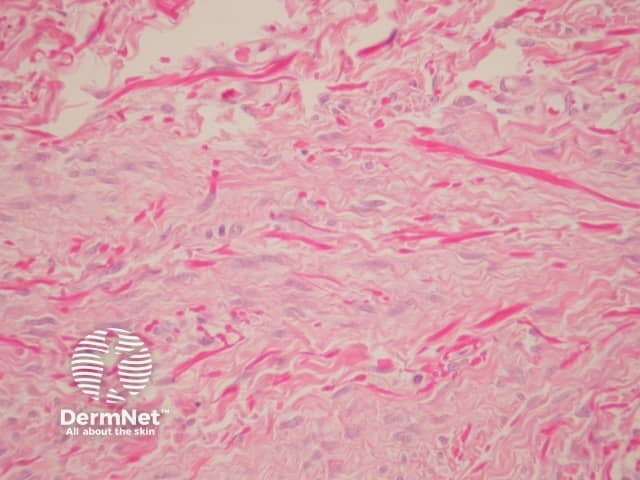
Figure 3
Special studies for dermatomyofibroma
Immunohistochemically, neoplastic cells may express some actin and CD34 positivity. Elastic fibres are increased which can be demonstrated with elastic stains.
Differential diagnosis of dermatomyofibroma pathology
Immunohistochemical studies may be used to exclude other spindle cell lesions. The lack of expression of S-100 excludes neurofibroma and desmoplastic spindle cell naevus. Lack of epithelial membrane antigen expression excludes perineurioma.
References
- Mentzel T, Kutzner H. Dermatomyofibroma: clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 56 cases and reappraisal of a rare and distinct cutaneous neoplasm. Am J Dermatopathol. 2009 Feb;31(1):44–9. PubMed
- Weedon’s Skin Pathology (Third edition, 2010). David Weedon
On DermNet
