Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Cupping — extra information
Cupping
Author: Steven Xie. Final year medical student. University of Auckland. Chief Editor: Dr Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, June 2015.
What is cupping?
Cupping is a form of alternative medicine, and has been practiced for thousands of years in China.
Cupping involves placing cups on the patient’s skin corresponding to the acupuncture points. The cups are made of glass, bamboo, or pottery.
The desired effect is to redden the local skin or achieve blood stasis at the site of treatment. It is thought in traditional Chinese medicine that this can potentially help with certain conditions and diseases.
There are a few different cupping techniques. The main type is called retained cupping, in which there is negative pressure in the cup. Usually this is done by igniting an alcohol-soaked cotton swab inside the cup, which creates a vacuum. The burning swab is removed, and the hot cup is placed on the skin, causing the skin to protrude.
Other cupping techniques include:
- Wet cupping (bleed cupping). This involves creating a small cut on the skin, before ensuring the cup has a suction effect when it is applied to the area.
- Suction devices
- Moving cupping
- Medicinal cupping
- Water cupping.
What is the cupping used to treat?
Cupping is used to treat numerous conditions, including headache, chronic pain, (eg back pain), herpes zoster, cough, common cold, asthma, urticaria, and menstrual irregularity. However, there is no clinical evidence to prove that cupping is effective for these conditions.
What is the effect of cupping on the treated skin?
Cupping results in circular red marks (erythema), bruises (ecchymoses, petechiae, and linear purpuric streaks) and abrasions.
A case of panniculitis has also been reported as an adverse effect.
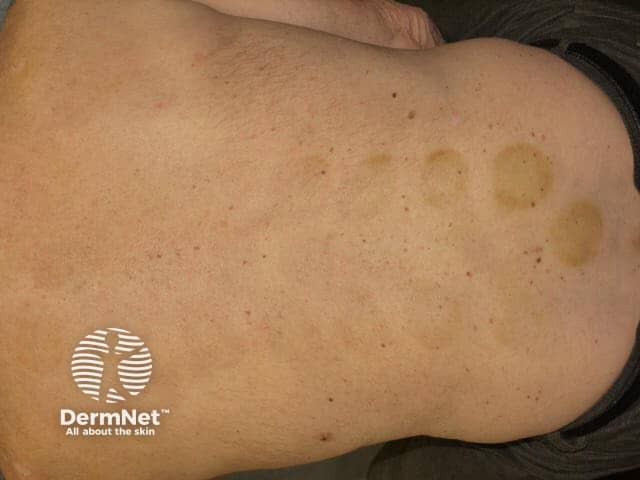
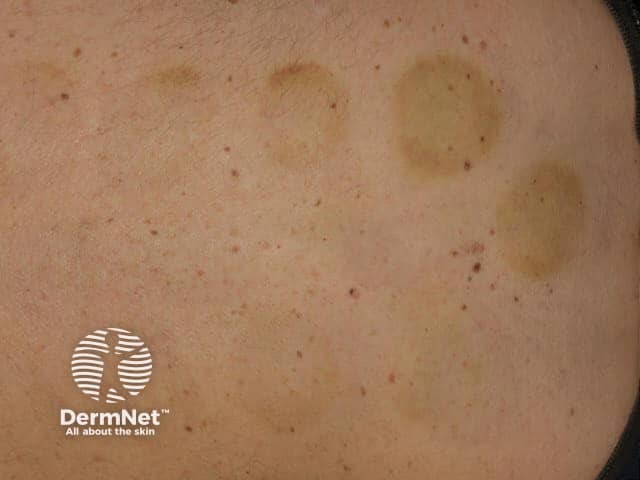
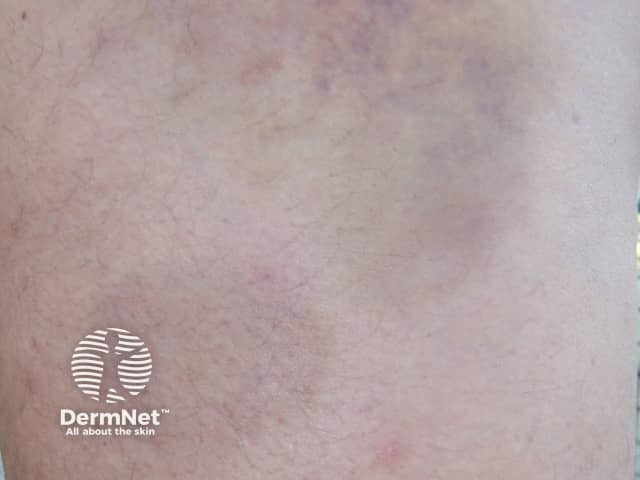
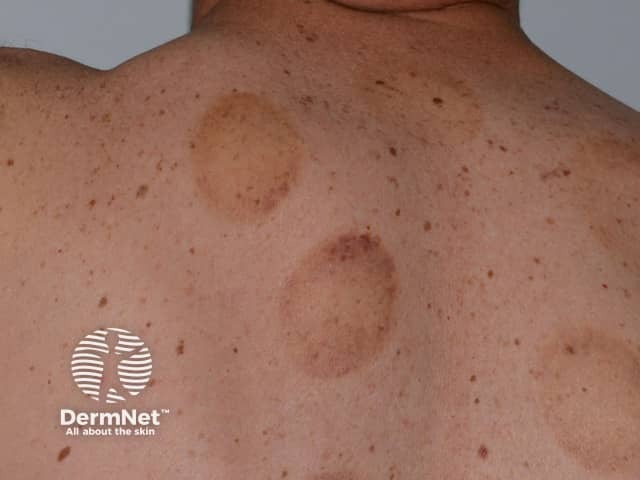
References
- Cao H, Han M, Li X, Dong S, Shang Y, Wang Q, Xu S, Liu J. Clinical research evidence of cupping therapy in China: a systematic literature review. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2010 Nov 16;10:70. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-10-70. Review. PubMed PMID: 21078197; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3000376.
- Lilly E, Kundu RV. Dermatoses secondary to Asian cultural practices. Int J Dermatol. 2012 Apr;51(4):372-9; quiz 379-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4632.2011.05170.x. Review. PubMed PMID: 22435423.
On DermNet
