Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Condyloma acuminatum pathology — extra information
Infections Diagnosis and testing
Condyloma acuminatum pathology
Author: Assoc Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand, 2013.
Introduction Histology Special stains Differential diagnoses
Introduction
Condyloma acuminatum is the name given to anogenital warts. They are usually sexually transmitted and are caused by human papillomavirus (HPV).
Histology of condyloma acuminatum
Histopathological examination of condyloma acuminatum reveals epidermal acanthosis. The surface has an undulated rounded papillomatosis rather than the spiked verrucous hyperplasia seen in verruca vulgaris (figure 1).
High power examination of condyloma acuminatum usually reveals vacuolated keratinocytes with shrunken nuclei (koilocytes) in the upper layers of the epidermis (figure 2). There may be enlarged keratohyaline granules as seen in other HPV-induced lesions.
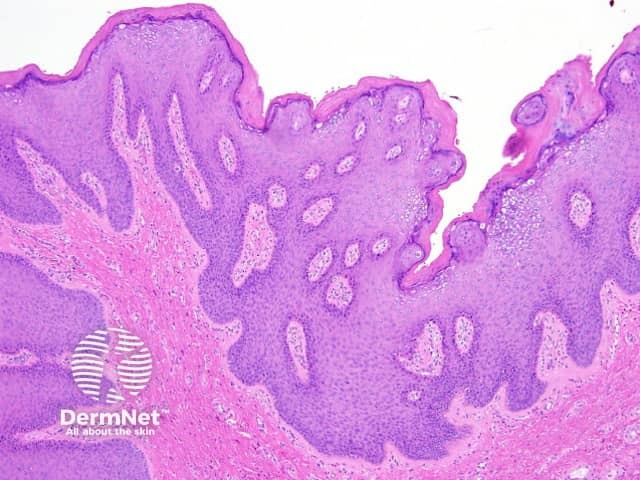
Figure 1
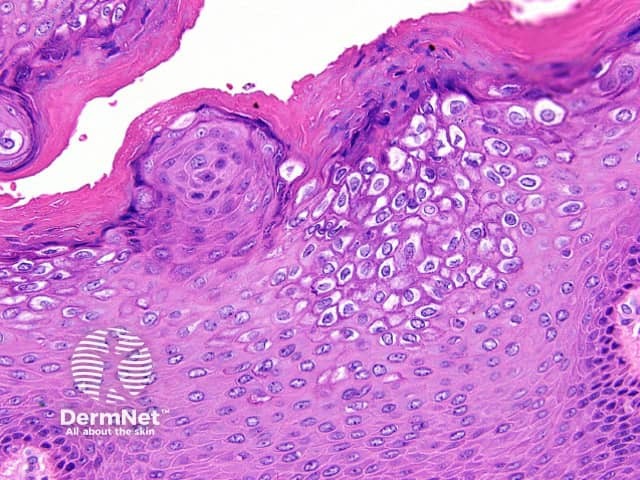
Figure 2
Special stains for condyloma acuminatum
In-situ hybridization for HPV or immunohistochemical studies for papillomavirus common antigen can help confirm the presence of HPV. PCR may be used to identify the HPV type.
Differential diagnosis of condyloma acuminatum pathology
Seborrhoeic keratosis – Distinction can be difficult for lesions without obvious koilocytes. Isolation of HPV and correlation with the clinical context can be helpful in some cases.
Verruca vulgaris – Sexually transmitted lesions caused by HPV types common in condyloma acuminatum may rarely cause epidermal lesions which closely resemble verruca vulgaris histologically.
References
- Weedon’s Skin Pathology (Third edition, 2010). David Weedon
- Pathology of the Skin (Fourth edition, 2012). McKee PH, J. Calonje JE, Granter SR
On DermNet
