Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Bronchogenic cyst pathology — extra information
Bronchogenic cyst pathology
Author: Assoc Prof Patrick Emanuel, Dermatopathologist, Auckland, New Zealand, 2013.
Introduction Histology Special studies Differential diagnoses
Introduction
Bronchogenic cysts originate from the ventral foregut that forms the respiratory system. They are located close to the trachea or main stem bronchi.
Histology of bronchogenic cyst
Bronchogenic cysts may be unilocular (figure 1) or multilocular. They may be located in the dermis or subcutis and occasionally drain into the overlying epidermis via a sinus. They are often filled with thick mucinous material and debris (figure 2).
The lining of the cyst is typically ciliated (figure 3, arrows) and may be columnar or cuboidal. Squamous metaplasia is common. In the wall, it is very common to find smooth muscle and respiratory-type mucous glands (figure 4). Cartilage is another common finding in the wall.
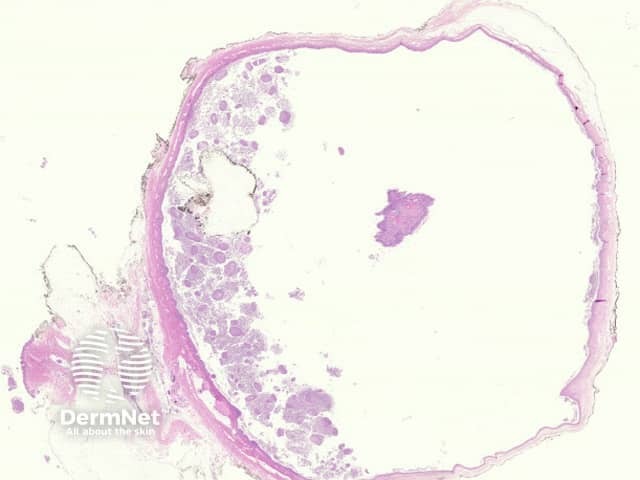
Figure 1
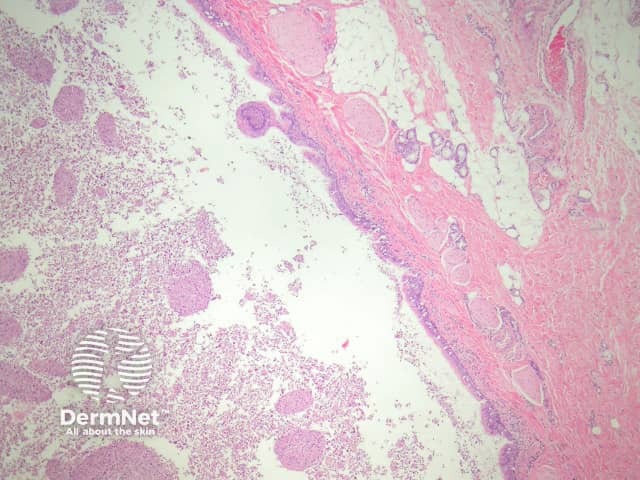
Figure 2
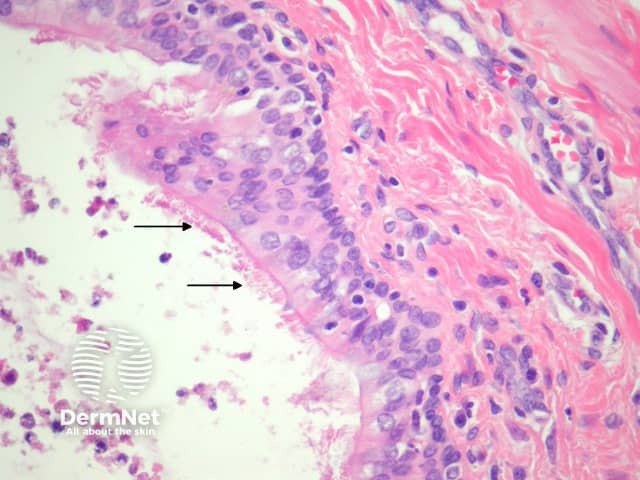
Figure 3
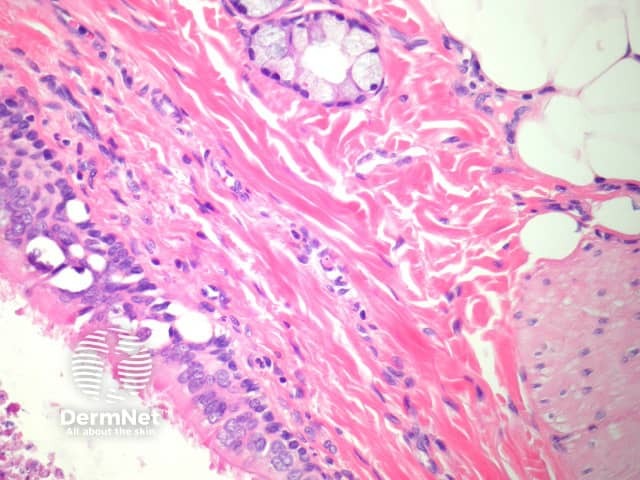
Figure 4
Special studies for bronchogenic cyst
None are needed.
Differential diagnosis of bronchogenic cyst pathology
Cutaneous ciliated cyst: Smooth muscle, mucous glands and cartilage are not seen in the walls of cutaneous ciliated cysts.
Branchial cleft cyst: Is usually squamous lined but may show foci of glandular epithelium with cilia. Typically the wall shows lymphoid tissue.
References
- Weedon’s Skin Pathology (Third edition, 2010). David Weedon
- Color atlas of dermatopathology (First edition, 2007). Jane M. Grant-Kels
On DermNet
