Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Allergy to para-tertiary butylphenol formaldehyde resin — extra information
Allergy to para-tertiary butylphenol formaldehyde resin
Author: Vanessa Ngan, Staff Writer, 2002.
What is PTBP formaldehyde resin and where is it found?
Clinical features
Diagnosis
Treatment
Prevention
Alternative names
Further information
Reference
What is para-tertiary butylphenol (PTBP) formaldehyde resin and where is it found?
PTBP formaldehyde resin is a phenol-formaldehyde resin that is mainly used in adhesives. It is ideally suited for this because it has very good binding qualities and has a particular tackiness for the surfaces of leather and rubber. For these reasons, PTBP formaldehyde is principally found in glued leather goods such as shoes, handbags, belts and watchstraps.
Other sources of PTBP formaldehyde resin include, DIY glues, varnish and lacquer resins, motor oil additives, rubber antioxidants, printing inks, fibreglass products, plywood, masonry sealant, insecticides, and deodorants and commercial disinfectants.
What are the reactions to PTBP formaldehyde resin allergy?
Typical allergic contact dermatitis reactions may occur in individuals allergic to PTBP formaldehyde resin. Rash is commonly found on the feet (shoe dermatitis) as the soles of shoes, particularly sponge rubber insoles in athletic shoes, are one of the most common sources of PTBP formaldehyde resin.
In people exposed to airborne PTBP formaldehyde resin in an occupational setting, the reaction may occur on exposed sites such as face and neck, and can lead to considerable swelling and blistering.
PTBP formaldehyde resin may also cause depigmentation.
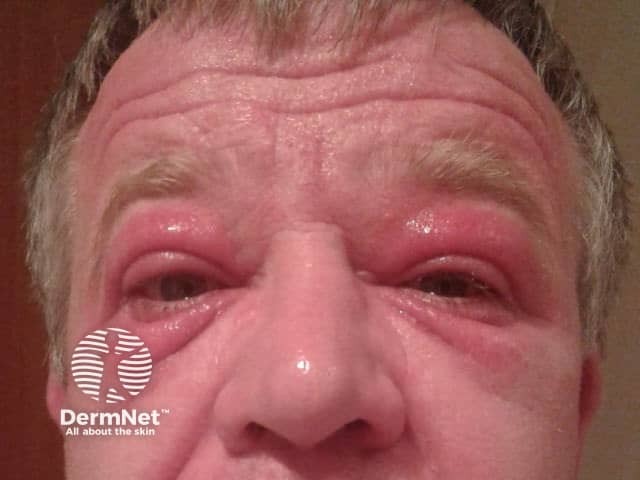
Contact allergy to para-tertiary butylphenol formaldehyde resin
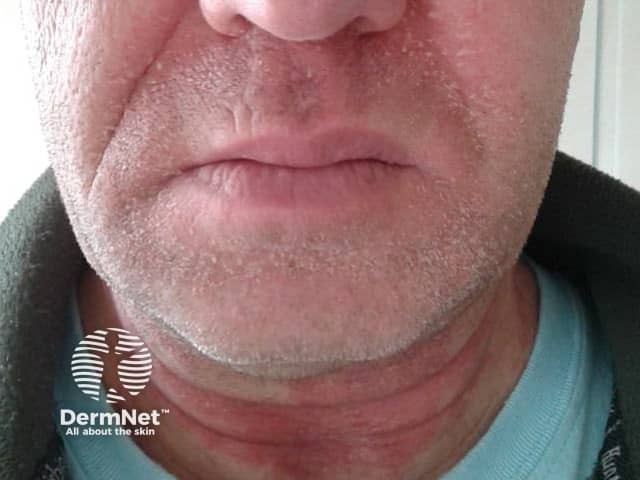
Contact allergy to para-tertiary butylphenol formaldehyde resin
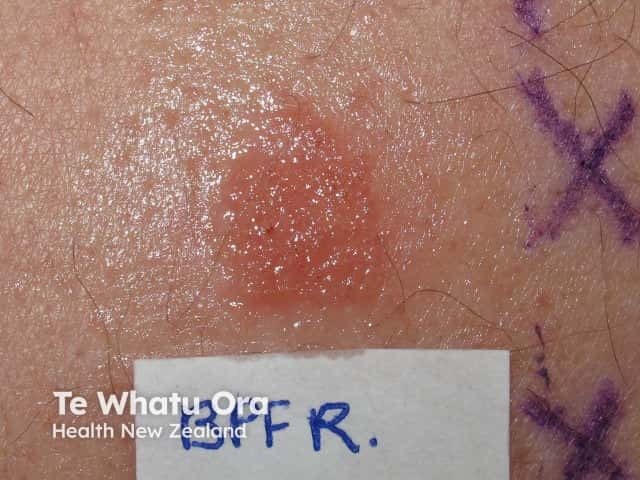
Positive patch test to PTBP formaldehyde resin
Am I allergic to PTBP formaldehyde resin?
PTBP formaldehyde resin allergy is diagnosed from the clinical history and by performing special allergy tests, i.e. patch tests with PTBP 1% in petrolatum.
Para-tertiary butylphenol is the sensitising agent in phenol-formaldehyde resins, not the phenol or formaldehyde. Sensitivity to formaldehyde does not imply allergy to formaldehyde resins.
Treatment of contact dermatitis due to PTBP formaldehyde resin exposure
If you are diagnosed with PTBP formaldehyde resin allergy then if at all possible avoid exposure to PTBP formaldehyde resin containing products, otherwise take measures to reduce potential exposure. Dermatitis appearing on the skin can be treated as for any acute dermatitis/eczema, i.e. topical corticosteroids, emollients, treatment of any secondary bacterial infection (Staphylococcus aureus), etc.
What should I do to avoid PTBP formaldehyde resin allergy?
Try to avoid getting any products containing PTBP formaldehyde resin wet as moisture causes breakdown of chemicals and release of PTBP allergen, thus allowing it to come into contact with skin. Always wear socks in your shoes. Try to avoid getting shoes wet or soaked by water. Also change socks regularly to avoid sweat from building up and dampening the shoes.
Wear gloves when working with glues or adhesives that contain PTBP formaldehyde resin or find a suitable alternative free of the allergen.
In the workplace try to avoid exposure to PTBP formaldehyde resin, however this may not be practicable. Identify potential sources of exposure using Material Safety Data Sheets; these are required for all chemicals and substances that you may come into contact with in the workplace. To reduce exposure, wear gloves to protect the hands.
Alert your doctor or dentist to the fact that you have an allergy to PTBP formaldehyde resin. Your dermatologist may have further specific advice, particularly if you are highly sensitive to PTBP formaldehyde resin.
Alternative names for PTBP formaldehyde resin
PTBP formaldehyde resin is also known by several other names. These include:
- p-tert- butylphenol formaldehyde resin
- PTBP formaldehyde
- Butylphen
- 4 (1,1-dimethylethyl) phenol
- 4-tert-Butylphenolformaldehyde resin
Avoid all of these. At work, request a material safety data sheet to help identify potential sources of exposure.
Further information
Sensitiser: para-tertiary butylphenol
Patch Test: 1% PTBP in petrolatum
Sources of Exposure to PTBP formaldehyde resin allergy
|
|
|
References
On DermNet
Other websites
- T.R.U.E. Tests
- Allergy New Zealand
- Allergic contact dermatitis – Medscape Reference
- Shoe allergies a personal resource for those allergic to their shoes
- Leather and Shoe Research Association of New Zealand
