Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Allergy to imidazolidinyl urea and diazolidinyl urea — extra information
Allergy to imidazolidinyl urea and diazolidinyl urea
Last Reviewed: January, 2025
Author(s): Dr Ishana Dixit, Northern Sydney Local Health District, Australia; Dr Shreya Andric, Northern Sydney Dermatology and Laser, Australia; Dr Zsófia Sára Hermann, Te Wao Nui Child Health Service and Hospital, Wellington, NZ (2025)
Previous contributors: Vanessa Ngan (2002)
Reviewing dermatologist: Dr Ian Coulson
Edited by the DermNet content department
Introduction
Demographics
Causes
Clinical features
Variation in skin types
Complications
Diagnosis
Differential diagnoses
Treatment
Alternative names
What are imidazolidinyl urea and diazolidinyl urea (DALU)?
Imidazolidinyl urea and DALU are formaldehyde-releasing preservatives used in many cosmetics and pharmaceutical preparations. They are commercially known as Germal 115 and Germal 11 respectively. Being structurally similar, cross reactivity between the two is common.
They are one of the most widely used preservative systems in the world and can be found in the following products:
Cosmetics
- Foundations, powders, concealers
- Eye makeup (liners, shadows, mascara)
- Facial makeup (blushes)
- Bronzers and tanning creams
- Makeup removers
- Cuticle removers
Self-hygiene/pharmaceutical products
- Burn remedies
- Shampoos
- Moisturizing lotions and creams
- Body powders
- Sunscreens
- Cleansers, wipes, and other skincare products
- Prescription topical medications
Household and industrial products
- Paints
- Cutting oils
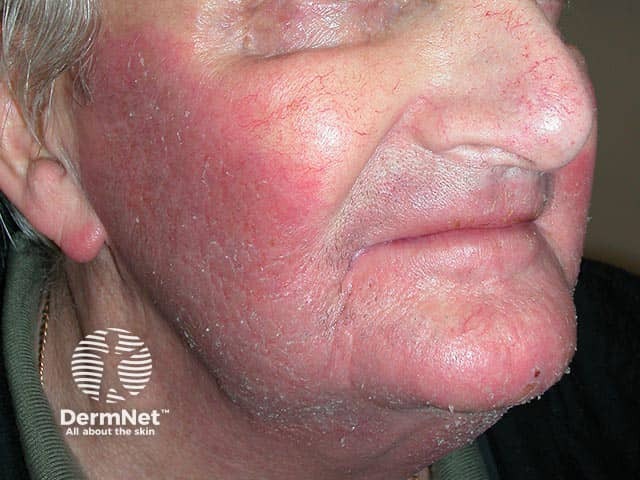
Allergic contact dermatitis on the face due to imidazolidinyl urea in a sunscreen
Who gets an allergy to imidazolidinyl urea and DALU?
An allergy to imidazolidinyl urea can develop in anyone. However, it is more common in:
- Atopic individuals
- Women (due to the presence of imidazolidinyl urea in cosmetics)
- Industrial workers involved in the handling of imidazolidinyl urea
- Individuals allergic to formaldehyde and other formaldehyde-releasing preservatives found in cosmetics, topical agents, and industrial and metalworking fluids
- Individuals with impaired barrier function of the skin eg, those with leg ulcers or chronic irritant dermatitis.
Imidazolidinyl urea is not a common cause of contact allergy when compared with other preservatives. For this reason, imidazolidinyl urea is often the preservative found in products that are labelled ‘hypoallergenic’. However, if you have a sensitivity to imidazolidinyl urea, these products are far from being hypoallergenic and should be avoided.
The true incidence of allergies to imidazolidinyl urea is unknown but reportedly seen in 1.9-3.2% of patch-tested individuals.
What causes allergy to imidazolidinyl urea and DALU?
Allergy to imidazolidinyl urea causes allergic contact dermatitis, a type IV hypersensitivity reaction. This mechanism involves CD4+ T-lymphocytes recognizing an antigen on the skin surface, which triggers the release of cytokines. These cytokines activate the immune system, leading to the development of dermatitis.
What are the clinical features of allergy to imidazolidinyl urea and DALU?
Allergy to imidazolidinyl urea typically presents with eczematous dermatitis localised to the site of contact. Skin lesions usually develop 48–72 hours after exposure and are generally confined to the contact area, though they may spread or become generalised.
The clinical features typically present in the following phases:
- Acute phase: Erythema, oedema and vesicles (sometimes bullae in severe cases)
- Subacute phase: Reduced erythema with the development of friable, peelable crusts and scales
- Chronic phase: Prolonged exposure may lead to lichenification (thickened, leathery skin).
Symptoms include intense itching, which is the most commonly reported issue, along with burning pain and swelling in some cases. These symptoms typically arise within hours of contact and resolve within days if the skin is no longer exposed to imidazolidinyl urea.
How do clinical features vary in differing types of skin?
Allergy to imidazolidinyl urea in darker skin tones may present as papulation, lichenification and pigmentary changes rather than erythematous patches and plaques. Furthermore, erythema may be disguised in darker skin tones (presenting as a grey or violaceous hue) resulting in delayed diagnosis.
What are the complications of allergy to imidazolidinyl urea and DALU?
Allergy to imidazolidinyl urea may result in the following complications:
- Secondary skin infections
- Autoeczemisation
- Erythroderma
- Chronic dermatitis — characterised by pigmentation changes, persistent pruritus and irritation and lichenification
- Worsening of pre-existing skin conditions such as atopic eczema or psoriasis.
How is allergy to imidazolidinyl urea and DALU diagnosed?
Allergy to imidazolidinyl urea and DALU is diagnosed based on the clinical history and by performing special allergy tests, i.e. patch tests. Patch testing with 2% imidazolidinyl urea in petrolatum is used.
Self-testing a product for imidazolidinyl urea is possible but should be done only after first talking with your doctor. This should be done only with products that are designed to stay on the skin such as cosmetics (not including eyeliners or mascaras) and lotions.
Apply a small amount of the product to a small area of skin such as the bend of your arm twice a day for 1 week. Examine the area each day and if no reaction occurs, repeat the test on a small area in front of your ear. If no reaction occurs, it is unlikely you are allergic to it. Even so, you should still be cautious if you intend to use it over large areas as it may be an irritant.
Products such as shampoos and cleansers should not be tested in this way as they may cause an irritant contact dermatitis if they are covered or overused on tender areas.
What are differential diagnoses for imidazolidinyl urea and DALU allergy?
Allergy to imidazolidinyl urea has the following differential diagnoses:
- Irritant contact dermatitis
- Seborrhoeic dermatitis
- Atopic dermatitis
- Psoriasis
- Drug eruptions
- Periorificial dermatitis
- Fungal infections
- Other forms/causes of dermatitis or urticaria.
What is the treatment for imidazolidinyl urea and DALU allergy?
Allergy to imidazolidinyl urea can be prevented and treated using the following methods:
Prevention
If diagnosed with imidazolidinyl urea allergy then one should avoid exposure to imidazolidinyl urea-containing products. This can be achieved by the following methods.
Reading product labels:
- Avoid products with imidazolidinyl urea or its alternative names
- Be wary of products that are labelled 'hypoallergenic' as these often contain imidazolidinyl urea
- If product ingredients are not fully listed, consult a pharmacist or contact the manufacturer for confirmation. Most companies list individual allergen constituents on their product website.
Avoiding formaldehyde and related preservatives found in cosmetics, topical agents, and industrial fluids, such as:
- Quaternium-15 (Dowicil®)
- DMDM hydantoin (Glydant®)
- Bromonitropropane diol (Bronopol™)
- Tris (hydroxymethyl) nitromethane (Tris Nitro®).
Using safe alternatives (provided there is no known allergy to these), such as:
- Methylparaben, ethylparaben, propylparaben, butylparaben, benzyl paraben (parabens)
- Methylchloroisothiazolinone
- Methylisothiazolinone
- Methyldibromoglutaronitrile/phenoxyethanol
- Sorbic acid
- Propylene glycol.
Treatment
Once dermatitis appears on the skin, treatment is as for any acute dermatitis:
- Topical corticosteroids
- Emollients
- Treatment of any secondary bacterial infection with topical or oral antibiotics
- Avoiding scratching and keeping nails trimmed — this prevents further irritation and secondary infection.
Alternative names for imidazolidinyl urea
Imidazolidinyl urea is also known by several other names. These include:
- N,N-methylenebis (N'-)1-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dioxo-4-imidazolidinyl urea
- Urea, N,N-methylenebis [N'-[3-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dioxo-4-imidazolidinyl]
- 1,1'-Methylenebis[3-[3-(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dioxo-4-imidazolidinyl]urea]
- Germall 115®
- Imidurea NF®
- Biopure 100®
- Imidurea®
- Sept 115®
- Tristat 1U®
- Unicide U-13®.
Bibliography
- Fonacier L, Bernstein DI, Pacheco K, Holness DL, Blessing-Moore J, Khan D, Lang D, Nicklas R, Oppenheimer J, Portnoy J, Randolph C, Schuller D, Spector S, Tilles S, Wallace D. Contact dermatitis: A Practice Parameter–Update 2015. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2015 May;3(3). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaip.2015.02.009. Journal
- Goossens A, Aerts O. Contact allergy to and allergic contact dermatitis from formaldehyde and formaldehyde releasers: A clinical review and update. Contact Dermatitis. 2022 Jul;87(1):20-27. doi: 10.1111/cod.14089. Epub 2022 Mar 17. PMID: 35229319. Journal
- Shaughnessy CN, Malajian D, Belsito DV. Cutaneous delayed-type hypersensitivity in patients with atopic dermatitis: reactivity to topical preservatives. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2014 Jan;70(1):102-7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2013.08.046. Journal
- Tramontana M, Hansel K, Bianchi L, Sensini C, Malatesta N, Stingeni L. Advancing the understanding of allergic contact dermatitis: from pathophysiology to novel therapeutic approaches. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 May 22;10:1184289. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1184289. PMID: 37283623; PMCID: PMC10239928. Journal
