Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf — extra information
Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf
Author: Dr Georgina Harvey, Dermatology Registrar, Waikato Hospital, Hamilton, New Zealand; Chief Editor: Dr Amanda Oakley, Dermatologist, Hamilton, New Zealand, October 2015.
What is acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf?
Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf is a rare genodermatosis classified as a disorder of keratinisation. It is often considered to be a variant of Darier disease. It was first identified in 1931 by Dr Gustav Hopf, a German dermatologist.
What is the cause of acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf?
Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf is due to an abnormal ATP2A2 gene. It has autosomal dominant inheritance, meaning that only one copy of the affected gene needs to be inherited to develop the disease. If one parent is affected, the chance of a child developing acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf is 1 in 2 (50%).
Mutations in ATP2A2 also cause Darier disease. The gene encodes the sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 2 pump, controlling intracellular calcium. It is hypothesised that impaired functioning of this pump alters the ability of desmosomes to link keratinocytes together.
What are the clinical features of acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf?
Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf is characterised by multiple, flat-topped, symmetrical, skin coloured keratotic lesions on the dorsum of the hands and feet. These are usually present from birth or early childhood but occasionally arise in adult life. Other features may include:
- Grouped or isolated papules on the knees, elbows and forearms
- Pits on the palms of the hands and soles of the feet
- Nail dystrophy: pearly white nails, or nails with longitudinal ridges and nicks in the free edge
The skin changes in acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf are asymptomatic and rarely lead to any complications.

Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf
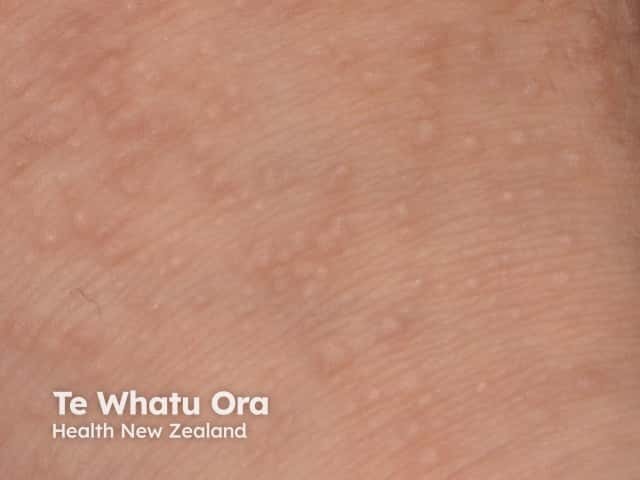

Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf
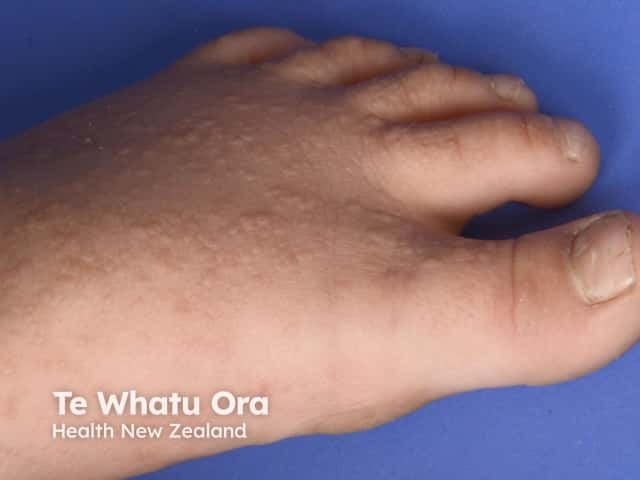
Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf
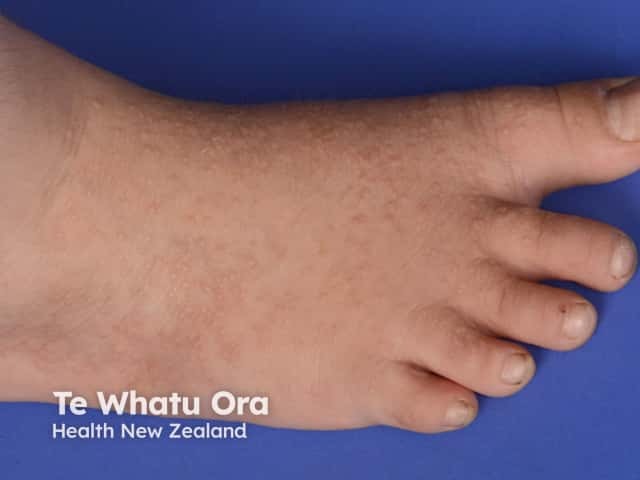
Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf
How is acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf diagnosed?
Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf is diagnosed clinically. This is easier if there are family members with similar skin findings. Sometimes a skin biopsy is performed to assist with the diagnosis.
The key features on histology are hyperkeratosis, acanthosis, papillomatosis and a thickened granular layer. Rarely, acantholysis is seen. Circumscribed epidermal elevations, known as 'church spires' are a distinctive finding. See Darier disease pathology.
What is the treatment for acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf?
As acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf is asymptomatic and localised, no treatment is required. If a patient prefers treatment for cosmetic reasons, destruction of the papules can be performed with cryotherapy or a destructive laser. Topical tretinoin has also been used to reduce the thickness of the papules.
References
- Agrawal SN, Jane SD, Rawal AA. Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf in family. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014 Nov;5(Suppl 1):S17-9. doi: 10.4103/2229-5178.144509. PubMed PMID: 25506556; PubMed Central
- Bang CH, Kim HS, Park YM, Kim HO, Lee JY. Non-familial Acrokeratosis Verruciformis of Hopf. Ann Dermatol. 2011 Sep;23 Suppl 1:S61-3. doi: 10.5021/ad.2011.23.S1.S61. Epub 2011 Sep 30. PubMed PMID: 22028575; PubMed Central
- Rallis E, Economidi A, Papadakis P, Verros C. Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf (Hopf disease): case report and review of the literature. Dermatol Online J. 2005 Aug 1;11(2):10. Review. PubMed
- Moshin A. Acrokeratosis verruciformis of Hopf — Medscape 2004
On DermNet
Other websites
