Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Causes of contact allergic dermatitis – 10 cases
This quiz will test your skills at identifying the cause of contact allergic dermatitis.
Contact allergic dermatitis results from delayed hypersensitivity to the responsible material. The dermatitis arises hours to days after contact and settles days to weeks later (rarely longer). It may have a variety of appearances. The rash may be confined to the site of contact but tends to spread more widely and may become generalised. Patch testing may reveal the cause but should be interpreted with caution and by experts.
Diagnosis is not always straightforward, as contact allergic dermatitis may resemble or complicate many other skin problems, particularly atopic dermatitis, venous dermatitis, nummular dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis. The patient may not have identified the cause, especially if he or she has been contact with the specific allergen without problem in the past. On the other hand, occupational dermatitis is more frequently due to contact with irritants than with allergens.
Please note: the images of patch test reactions are not always of the same patient described in the text.
For each of the ten cases, study the image(s) and then answer the questions. You can click on the image to view a larger version if required.
Each case should take approximately 2 minutes to complete. There is a list of suggested further reading material at the end of the quiz.
When you finish the quiz, you can download a certificate.
Case 1
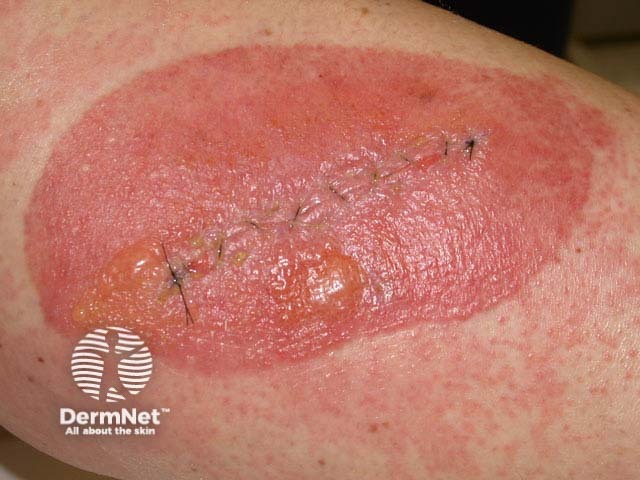
What material is this patient allergic to?
Allergy to colophony (rosin)
How would you confirm this?
The image shows a well-demarcated blistering eruption around a recent surgical wound, with some extension of erythema onto surrounding skin. The dermatitis was initially thought likely to be due to the skin cleanser used prior to the procedure or to the dressing applied afterwards. However, patch testing (figure 2) revealed contact allergy to colophony (rosin), a balsam or sticky material derived from pine trees. The dermatitis was caused by Friar's balsam (benzoin compound tincture), which had been applied prior to adhesive strips used to support the wound.
