Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Chronic forms of psoriasis
Created 2009.
Learning objectives
- Describe the clinical features and management of chronic forms of psoriasis
Note. You should have already read the overview page about psoriasis.
Clinical features
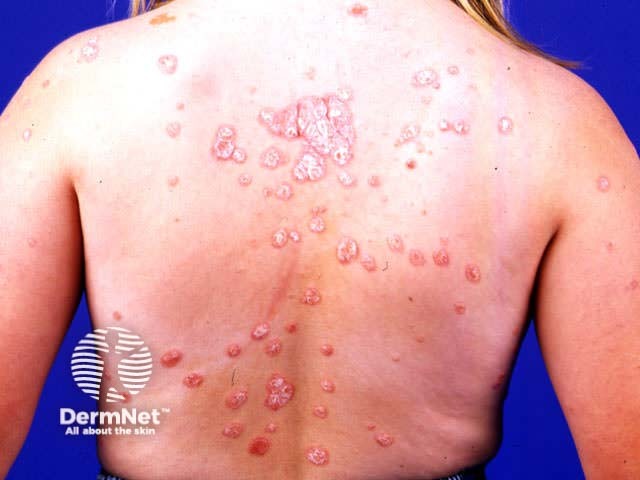
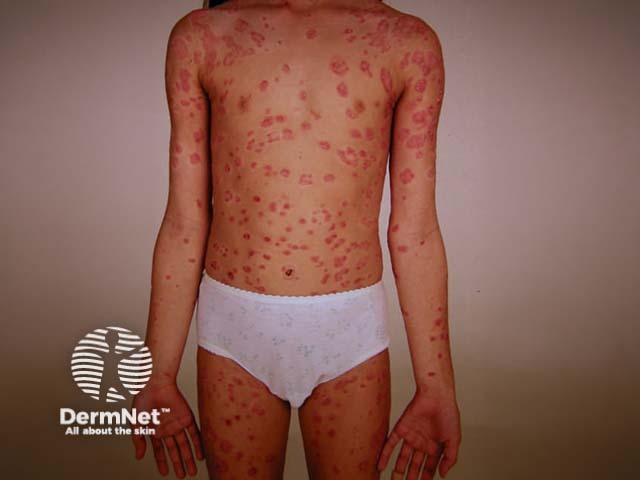
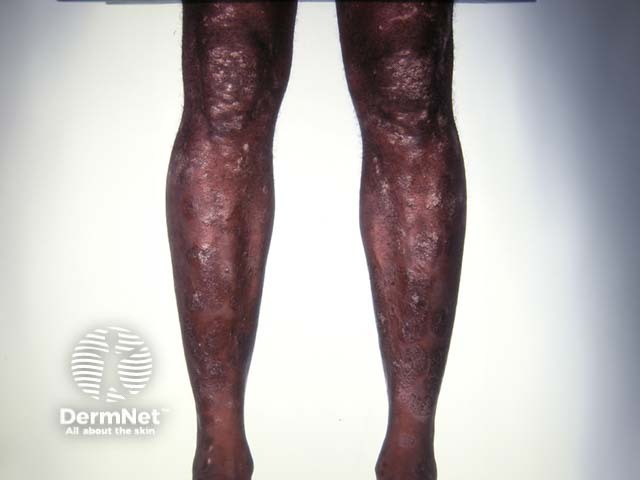
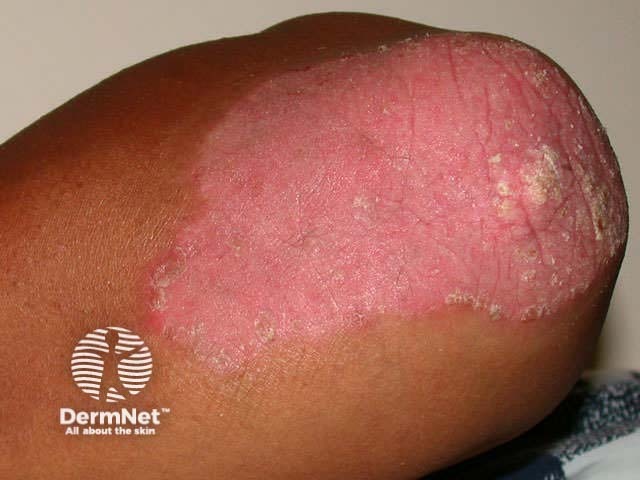
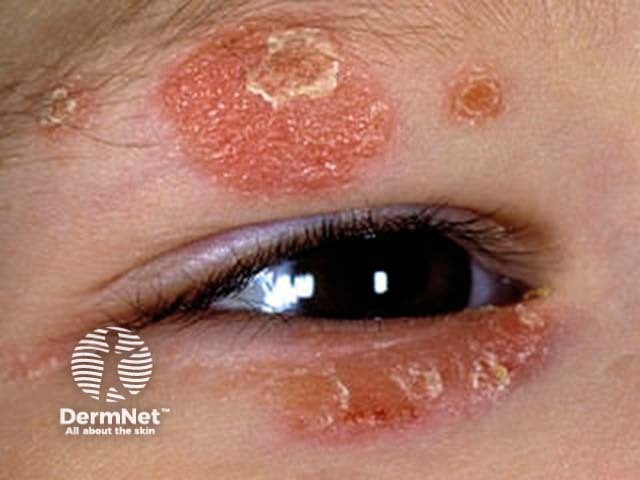
Chronic plaque psoriasis
Chronic plaque psoriasis is the most common form of psoriasis and is characterised by:
- Well-demarcated plaques on scalp, trunk and limbs
- Symmetrical distribution, most often on extensor elbows, knees, sacrum and scalp
- Variable number and size of lesions
- Variable erythema, induration and degree of scaling
Range of appearance of chronic plaque psoriasis
© R Suhonen 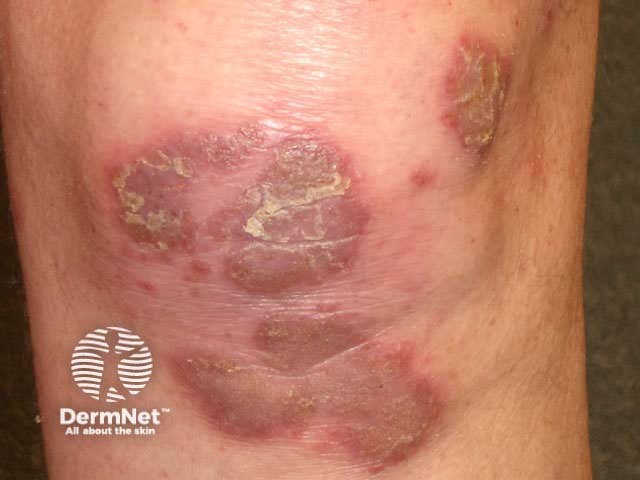
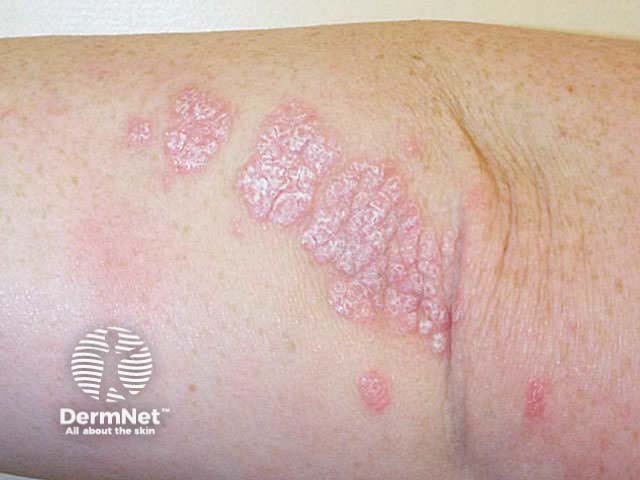
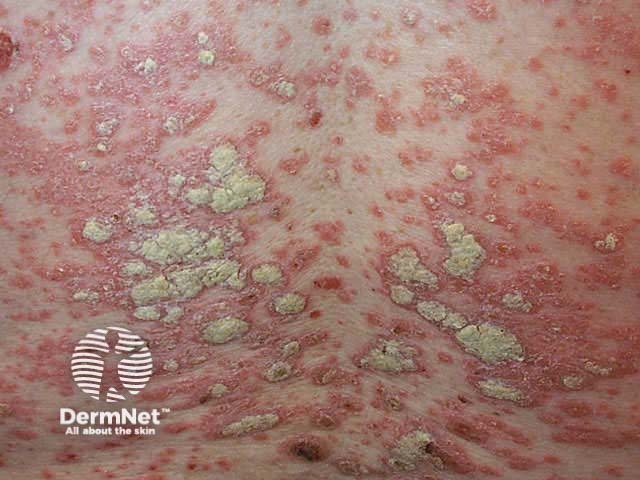
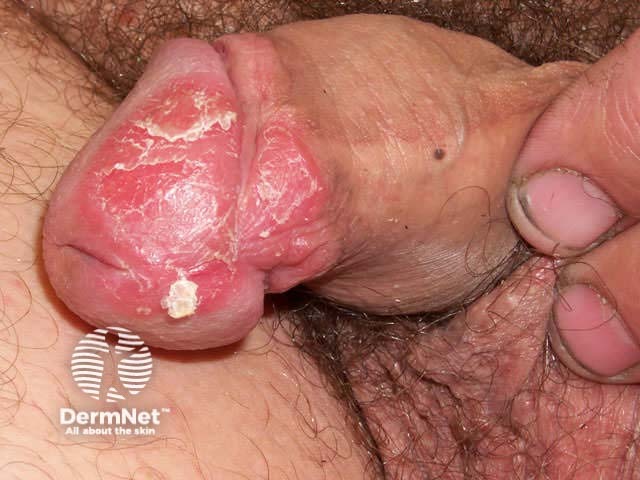
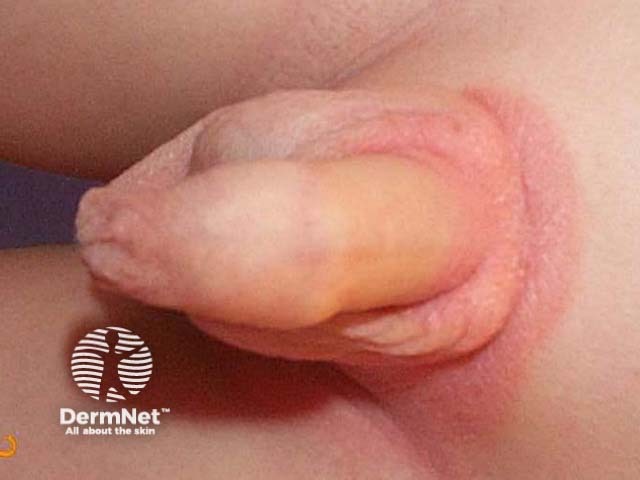
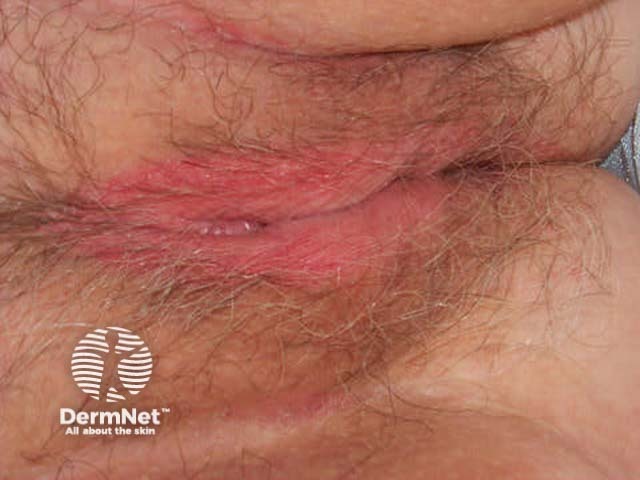
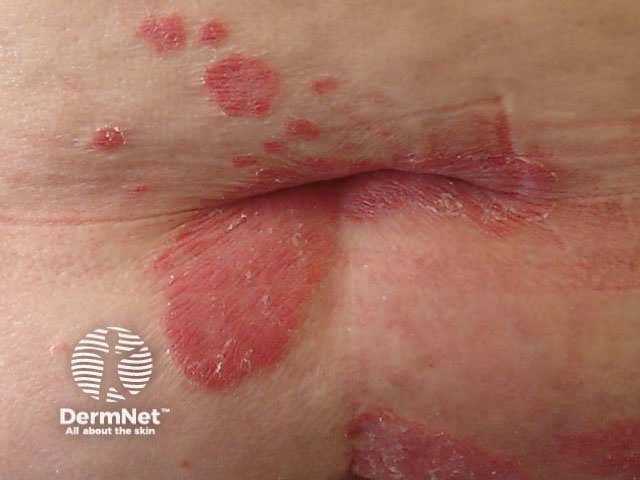
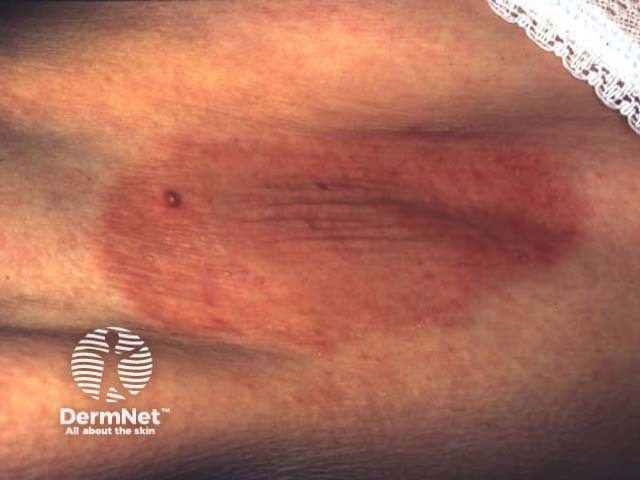
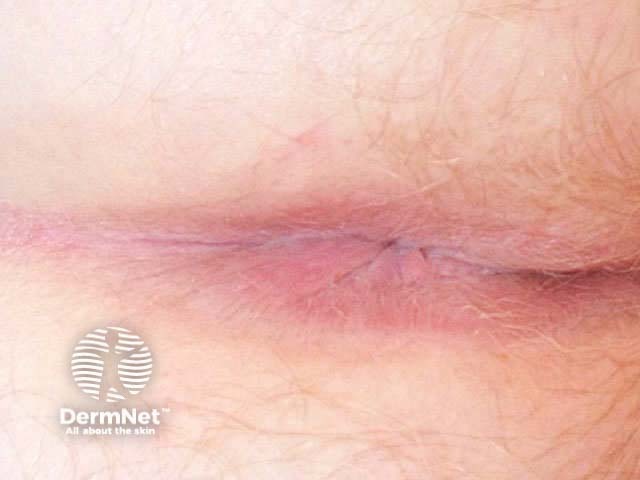
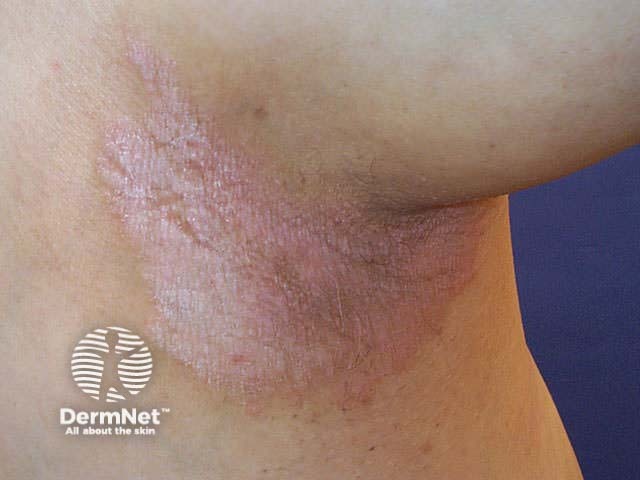
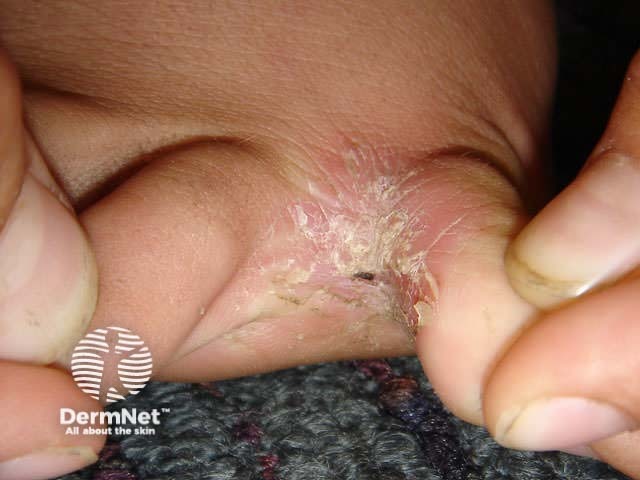
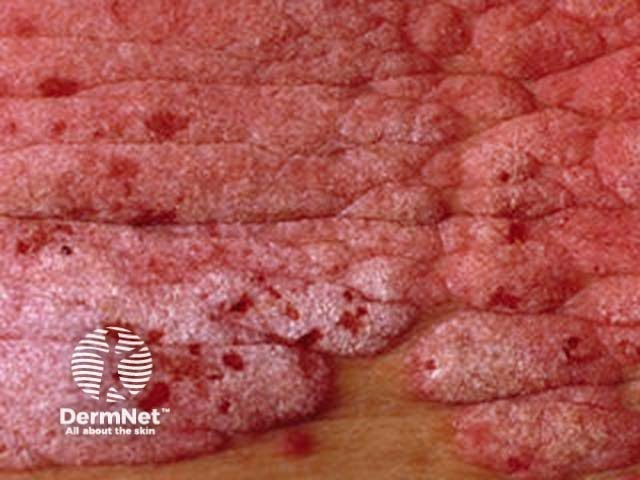
Flexural psoriasis (inverse psoriasis)
Flexural psoriasis is characterised by:
- Symmetrical chronic erythematosus shiny plaques in body folds especially axillae, inguinal folds, genitocrural sites, umbilicus, submammary areas
- Minimal scaling in most cases
- May arise in napkin area of infant, clearing with toilet training
- Often relatively asymptomatic despite impressive appearance
- May be colonised or infected with Candida species
'Inverse' psoriasis
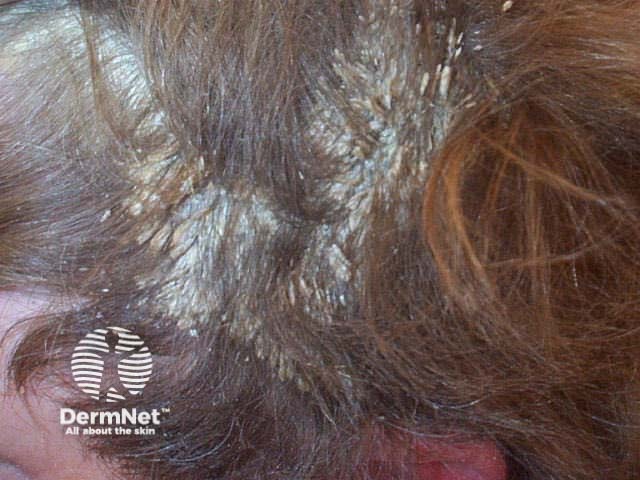
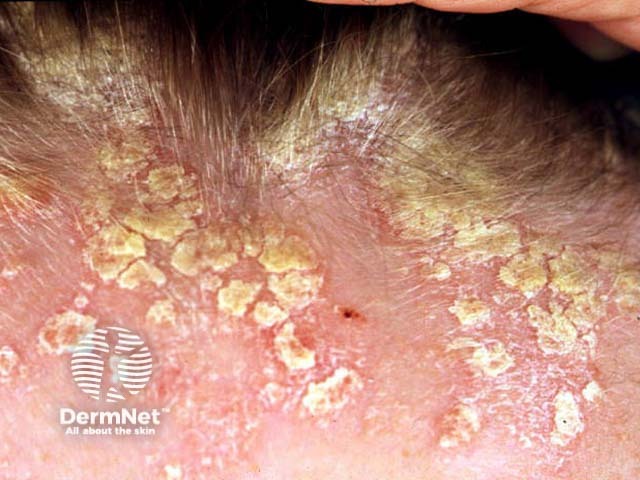
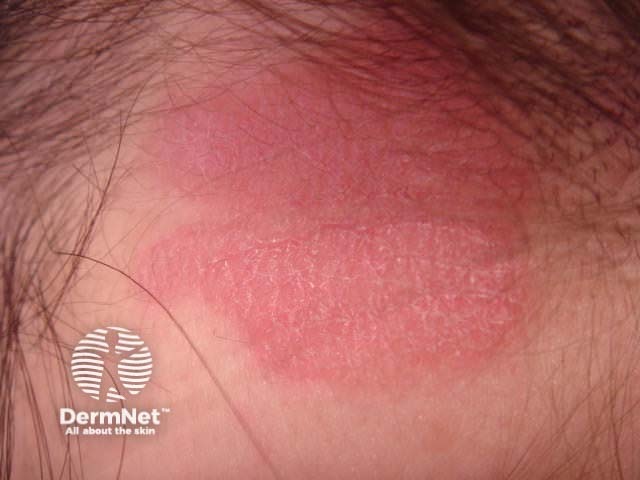
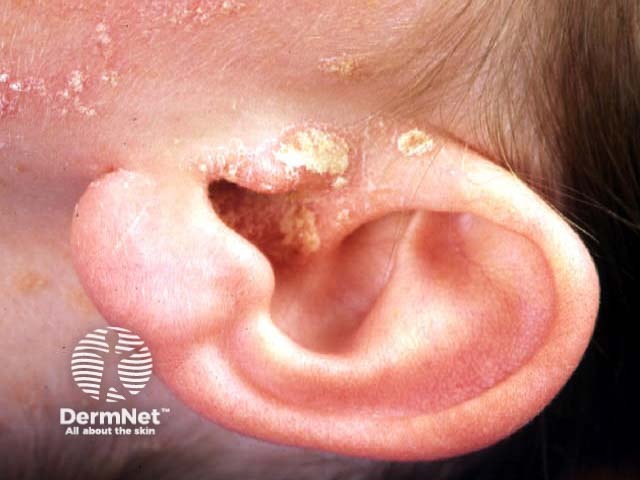
Scalp psoriasis
Scalp psoriasis may precede psoriasis in other sites by months or years. Typically, scalp psoriasis causes well demarcated erythematosus plaques with silvery white scaling.
The term ‘sebopsoriasis’ is used when the eruption ressembles seborrhoeic dermatitis (diffuse yellowish scale and little inflammation in scalp, diffuse scaling rash behind and inside ears, nasolabial folds, medial cheeks, eyebrows, anterior chest) but has a poor response to anti-dandruff shampoos.
Scalp psoriasis
© R Suhonen 
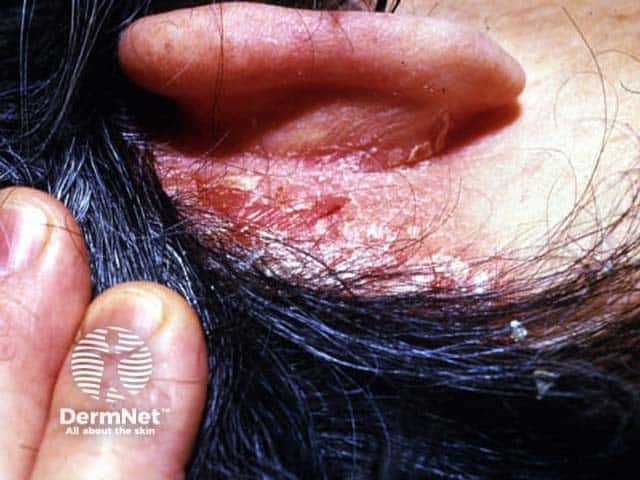
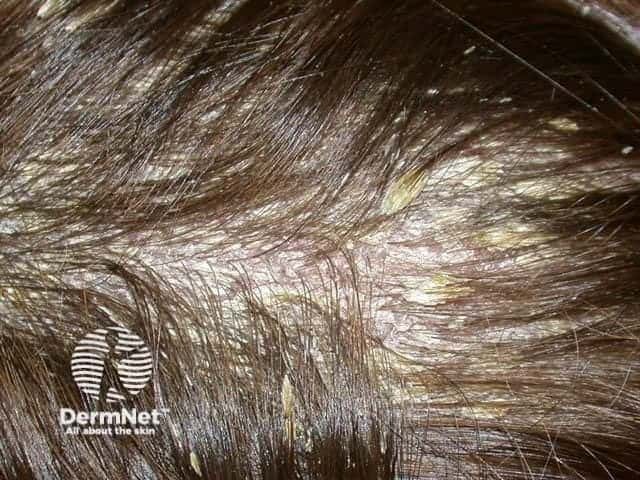
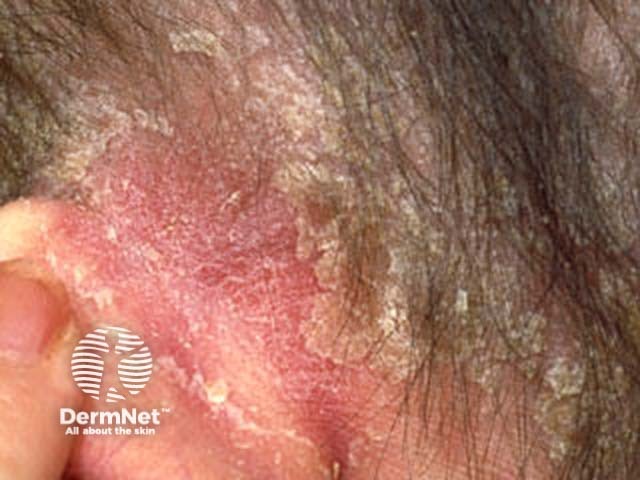
Other forms of plaque psoriasis
Uncommon subtypes of chronic plaque psoriasis include:
- Annular psoriasis: ring-shaped plaques with central clearing
- Rupioid psoriasis: limpet-like cone-shaped plaques
- Lichenified psoriasis: thickened scratched psoriasis (eczematised)
- Elephantine psoriasis: persistent, leathery, large plaques
- Ostraceous psoriasis: very thickly scaled plaques resembling an oyster shell
- Photosensitive psoriasis: psoriasis most severe in sun-exposed areas
Other forms of psoriasis
Annular psoriasis Ostraceous psoriasis Elephantine psoraisis 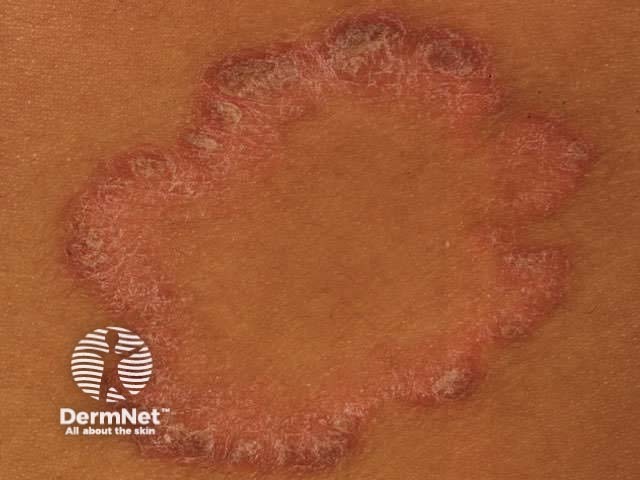
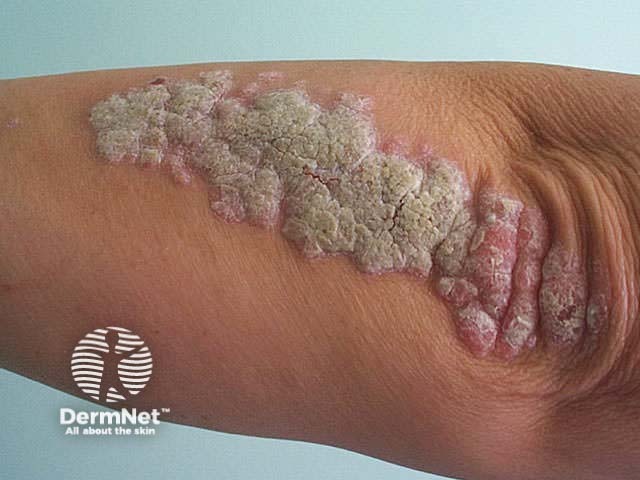
Management
It is most important to explain the nature of psoriasis to the patient presenting with psoriasis for the first time. Provide them with written material and refer them to DermNet (http://www.dermnetnz.info/) for further information. They need to be aware that there is no known cure and that psoriasis may persist lifelong. Treatment rarely results in complete clearance but reduces the severity and extent of the disease.
Mild chronic plaque psoriasis is usually managed with topical agents.
- Calcipotriol ointment for scaly plaques, cream for flexures (not face)
- Coal tar and salicylic acid ointment, cream or gel
- Short contact dithranol cream for a small number of larger plaques (not suitable for flexures)
- Intermittent potent or ultrapotent topical steroids (e.g. 2-week courses and/or pulse treatment once or twice daily on Saturday and Sunday each week)
- Mild topical steroids or calcineurin inhibitors on face
- Intermittent topical steroid / imidazole combination cream for flexures
If plaque psoriasis is too extensive or severe to be effectively managed with topical treatments alone, refer to a dermatologist for phototherapy and/or systemic agents.
Options for scalp psoriasis include:
- Shampoos containing coal tar and salicylic acid (ketoconazole and other anti-dandruff formulations are cleaner but less effective)
- Calcipotriol solution (cream for hairline) twice daily
- Coal tar and salicylic acid ointment, cream or gel applied for one to eight hours
- Intermittent potent or ultrapotent topical steroid lotions or solutions (e.g. pulse treatment Saturday and Sunday)
Activity
Investigate the role of dietary management of psoriasis (including ethanol, gluten-free and low-energy diets, polyunsaturated fatty acids).
References:
On DermNet:
Information for patients
Other websites:
- Medscape Reference: Psoriasis, plaque
- Merck Manual Professional: Psoriasis
Books about skin diseases:
See the DermNet bookstore
