Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Widespread rash following antibiotic and antifungal treatment
Last reviewed: June 2023
Author: Dr Stanley Leong, Dermatology and Paediatric Registrar, 2023. Reviewing dermatologist: Dr Ian Coulson (2023)
Edited by DermNet content department
Background
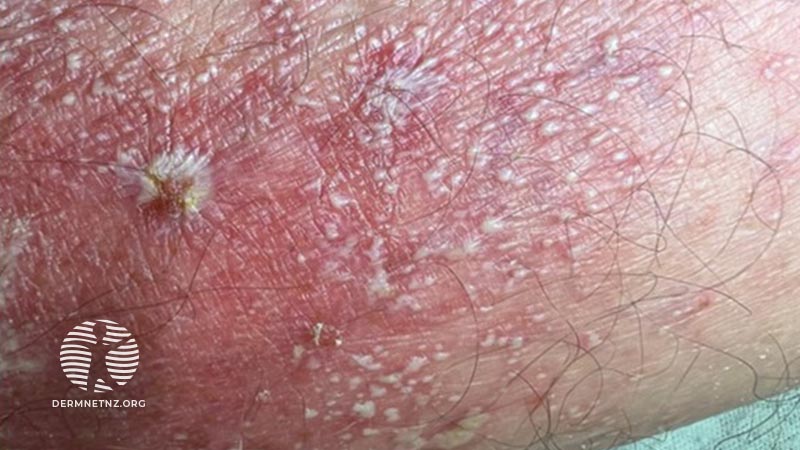
A 52-year old gentleman presented with widespread rash of one week's duration - it started 3 days following commencement of oral flucloxacillin and fluconazole for oral thrush and possible candida infection at the groin.
On examination, there was desquamation on the palm, and erythema studded with multiple tiny pustules coalescing into larger pustular lakes on the trunk and limbs.
What is the diagnosis?
Acute generalised exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), also known as toxic pustuloderma.
AGEP is an uncommon pustular drug eruption characterised by superficial pustules coalescing to form pustular lakes on an erythematous base. There is superficial epidermal detachment in areas where the pustules have become confluent. The time interval between drug ingestion and onset is short (2–3 days).
Occasionally it may be localised to limited areas of skin such as the face (acute localised exanthematous pustulosis)
What are the possible causes?
Over 90% cases of AGEP are provoked by medications, most often beta-lactam antibiotics (eg, penicillins, cephalosporins).
Other medications include tetracyclines, sulfonamides, oral antifungals, hydroxychloroquine, carbamazepine, calcium-channel blockers and more.
Viral infections such as EBV, CMV, Hepatitis B, adenovirus and enterovirus are also common triggers of AGEP in children.
