Main menu
Common skin conditions

NEWS
Join DermNet PRO
Read more
Quick links
Tinea barbae — extra information
What is tinea barbae?
Tinea barbae is the name used for infection of the beard and moustache areas of the face with a dermatophyte fungus. It is less common than tinea capitis and generally affects only adult men.
The cause of tinea barbae is most often a zoophilic (animal) fungus:
- T. verrucosum (originating from cattle)
- T. mentagrophytes var. equinum (originating from horses)
Tinea barbae is usually due to infection of coarse facial hair with an ectothrix pattern (spores on the outside). In ectothrix infections, the fungal filaments (hyphae) and spores (arthroconidia) cover the outside of the hair.
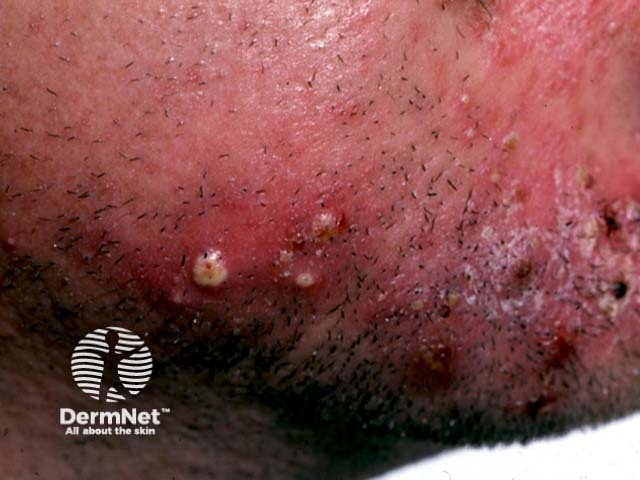
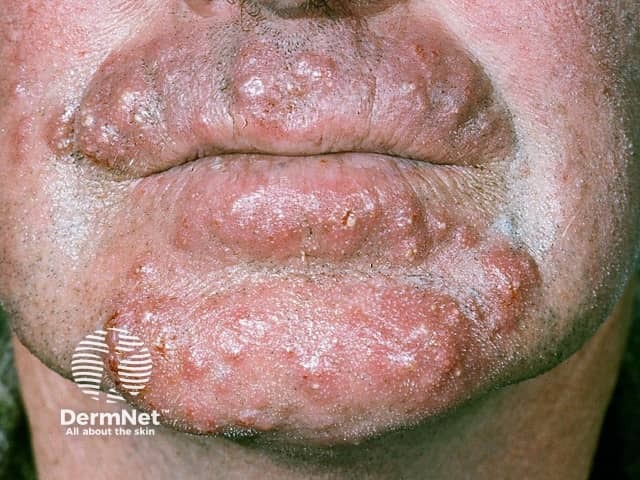
Fungal beard infection
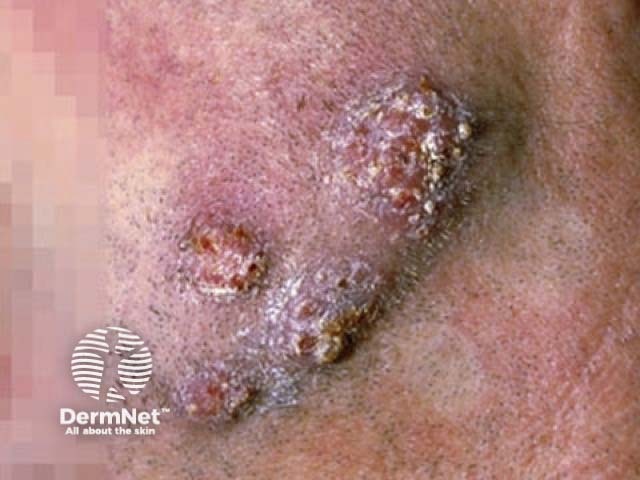
Tinea barbae
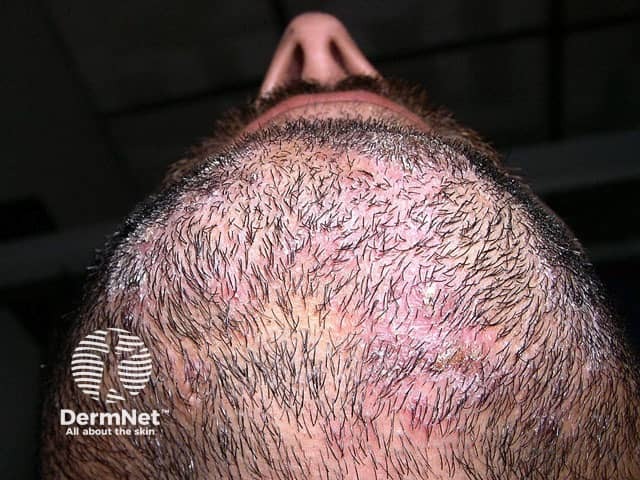
Image supplied by Dr Shahbaz A. Janjua
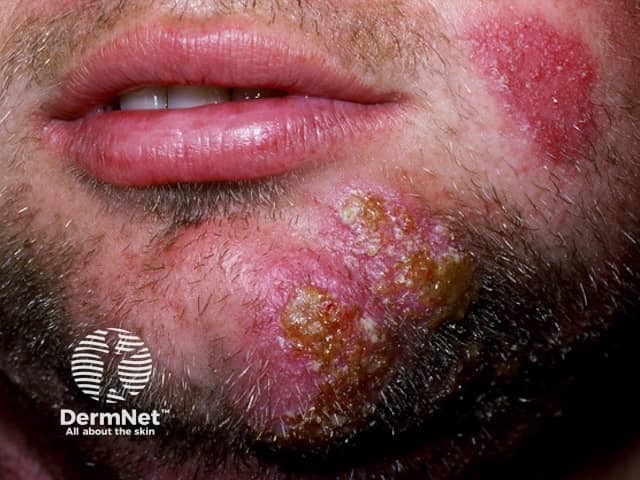
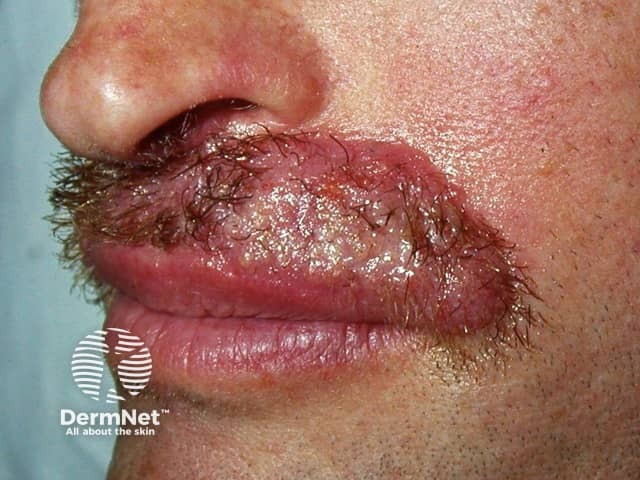
Fungal beard infection
Fungal beard infection
Fungal beard infection
Clinical features of tinea barbae
Tinea barbae most often affects farmers and is due to direct contact with an infected animal. It is rarely passed from one person to another.
Tinea barbae is usually very inflamed with red lumpy areas, pustules and crusting around the hairs (kerion). The hairs can be pulled out easily. Surprisingly, it is not excessively itchy or painful.
Tinea barbae can result in an id reaction, especially just after starting antifungal treatment.
Diagnosis of tinea barbae
The diagnosis of tinea barbae is confirmed by microscopy and culture of skin scrapings and hair pulled out by the roots.
Treatment of tinea barbae
Topical antifungal agents may be adequate for mild cases of tinea barbae, but it is usually treated with oral antifungal medicines, including terbinafine and itraconazole.
On DermNet
- Tinea
- Introduction to fungal infections
- Laboratory tests for fungal infections
- Treatment of fungal infections
Other websites
- Tinea barbae — Medscape Drugs & Diseases
Books about skin diseases
